Pollution
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Pollution is the harmful chemicals that go into the environment usually made by humans.
About Pollution
- Pollution can be in the water or in the air.
- Factories often produce pollution that gets into the air, including soot that can affect our breathing as well as Sulphur Dioxide and Nitrous Oxides which cause acid rain.
- Plastic is currently considered a major pollution in the oceans and is responsible for the deaths of countless animals every year.
- Fertilisers used on crops is a major source of pollution for rivers and lakes and can cause eutrophication.
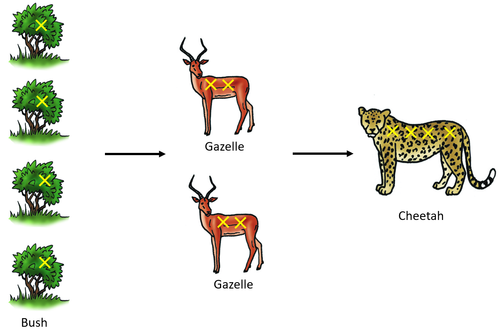
Pollution in a Food Chain
- When farmers grow crops, wild animals sometimes eat them, so the farmers spray the crops with poison.
- When the animals die from the poison, they are eaten by other animals which then also eat the poison.
- The poison builds up in the food chain, meaning the top carnivore often has a lot more poison than was originally sprayed on the crops. This can be very harmful to them and even kill them.
| In this diagram the poison is shown by yellow X's. If each gazelle eats two bushes, then the gazelles will get twice as much poison as the bush. If a cheetah eats two gazelles, then the cheetah will get twice as much poison as the gazelle had. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Pollution is the harmful chemicals that go into the environment (usually made by humans).
About Pollution
- There are many different kinds of pollution. Some go into the air where they can be inhaled by organisms, some go in the water where they can be ingested by animals or absorbed by plants and some may get into the soil where they can also be absorbed by plants.
- Pollutants can harm the organism which first takes them in or it can harm organisms further along in the food chain as the pollution can be concentrated as it is passed along to the next trophic level.
- Pollution can damage entire ecosystems and reduce biodiversity.
Pollution and Disease
- Air pollution is a risk factor in lung diseases including Lung Cancer.
References
AQA
- Pollution, page 116, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Pollution, page 358-61, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Pollution, pages 202-203, 217, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Pollution, pages 237-8, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Pollution, pages 263, 264, 271-6, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Pollution, pages 276, 277, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Pollution, pages 288-291, 296-297, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Pollution, pages 341, 342, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Pollution, pages 91, 158, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Pollution; indicator, page 360-1, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Pollution; Of air, pages 105, 179-81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Pollution; Of land, pages 105-6, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Pollution; Of water, pages 104-5, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Pollution, page 67, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Pollution, page 93, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Pollution, pages 158-159, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Pollution, pages 283, 308, 309, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Pollution, pages 95, 105, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Pollution; assessing, pages 186-187, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel