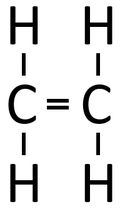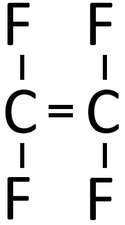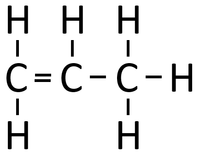Polymerisation
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Polymerisation is a chemical reaction in which small molecules known as monomers react to form a polymer.
About Polymerisation
Polymerisation may happen between:
- Identical monomers - Alkenes to Polyalkenes
- Two different monomers with complimantary functional groups at each end. - Esters to Polyesters
- Several different monomers of a homologous series - Peptides to Polypeptides.
Examples
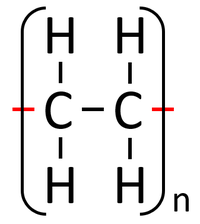
| Ethene monomers can react together in an Addition Polymerisation reaction. | Polythene (sometimes spelled Polyethene) is formed. |
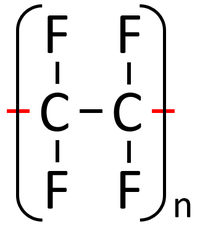
| Tetrafluoroethene monomers can react together in an Addition Polymerisation reaction. | Polytetrafluoroethene (sometimes referred to as PTFE or by the trademark TeflonTM) is formed. |
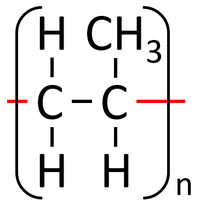
| Propene monomers can react together in an Addition Polymerisation reaction. | Polypropene is formed. |
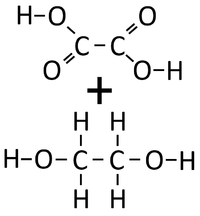
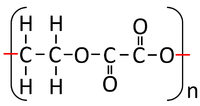
| Ethandioate and Ethandiol can react together in a Condensation Polymerisation. | A Polyester is formed along with Water. |
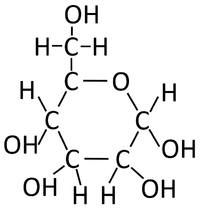
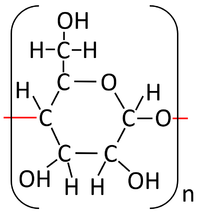
| Glucose molecules react together in a Condensation Polymerisation reaction. | Starch is formed along with Water. |
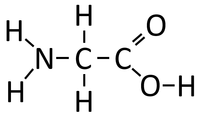
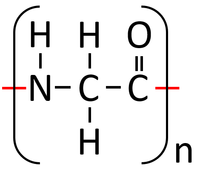
| Glycine molecules react together in a Condensation Polymerisation reaction. | A Polypeptide (Protein) is formed along with Water. In reality Polypeptides are made of many different Peptides (Amino Acids) rather than the same one repeated. |