Difference between revisions of "Electrical Transformer"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== right|300px|thumb|A picture of a '''transformer''' in the [[National Grid.]] A '''transformer''' is a device used to tak...") |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===About Transformers=== | ===About Transformers=== | ||
: '''Transformers''' use a coil of [[wire]] in one [[circuit]] (primary coil) wrapped around a [[Soft Iron|soft iron]] core and second coil of [[wire]] in another [[circuit]] (secondary coil). When an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]] passes through the primary coil this creates a changing [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] which induces an alternating [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the secondary coil. If that secondary coil is connected in a [[circuit]] it will produce an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]]. | : '''Transformers''' use a coil of [[wire]] in one [[circuit]] (primary coil) wrapped around a [[Soft Iron|soft iron]] core and second coil of [[wire]] in another [[circuit]] (secondary coil). When an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]] passes through the primary coil this creates a changing [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] which induces an alternating [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the secondary coil. If that secondary coil is connected in a [[circuit]] it will produce an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]]. | ||
| + | : There are two types of '''transformer''' you should know: | ||
| + | :*Step Up '''Transformer''' - A '''transformer''' which increase the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]]. | ||
| + | :*Step Down '''Transformer''' - A '''transformer''' which decrease the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]]. | ||
| + | : Step up '''transformers''' are used in the [[National Grid]] to increase the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] and decrease the [[Electrical Current|current]] for long distance transmission. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 12: | Line 16: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] of a '''transformer''' shows that an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]] in the primary coil induces an alternating [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] in the secondary coil. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] of a '''transformer''' shows that an [[Alternating Current|alternating current]] in the primary coil induces an alternating [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] in the secondary coil. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Equation=== | ||
| + | ''NB: You must be able to use this equation, but you do not need to remember it.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | (Primary Potential Difference)/(Secondary Potential Difference)=(Primary Coils)/(Secondary Coils) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{n_p}{n_s}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_p</math> = The [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the primary coil. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_s</math> = The [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the secondary coil. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>n_p</math> = The number of loops on the primary coil. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>n_s</math> = The number of loops on the secondary coil. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |[[File:TransformerQ1.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:TransformerQ2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:center;" |Calculate the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the secondary coil. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:center;" |Calculate the [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] across the secondary coil. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in [[SI Unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_p</math> = 3V | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>n_p</math> = 4 coils | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>n_s</math> = 8 coils | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in [[SI Unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_p</math> = 9V | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>n_p</math> = 6 coils | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>n_s</math> = 8 coils | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers and [[Evaluate (Maths)|evaluate]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{n_p}{n_s}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{3}{V_s} = \frac{4}{8}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{3}{V_s} = 0.5</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers and [[Evaluate (Maths)|evaluate]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{n_p}{n_s}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{9}{V_s} = \frac{6}{8}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\frac{9}{V_s} = 0.75</math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''3. [[Rearrange (Maths)|Rearrange]] the equation and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>0.5 \times V_s = 3</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_s = 6V</math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width: 300px; text-align:left;" |'''3. [[Rearrange (Maths)|Rearrange]] the equation and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>0.75 \times V_s = 9</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>V_s = 12V</math> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 5 March 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning

A transformer is a device used to take the alternating current in a circuit and transmit it to another circuit to produce electricity with a different potential difference and current.
About Transformers
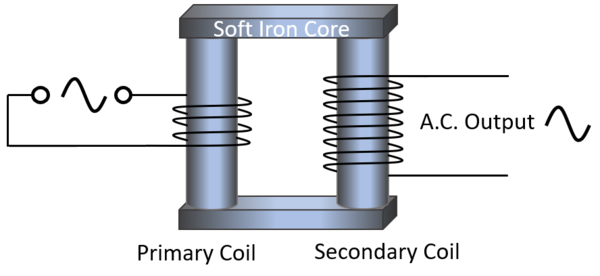
- Transformers use a coil of wire in one circuit (primary coil) wrapped around a soft iron core and second coil of wire in another circuit (secondary coil). When an alternating current passes through the primary coil this creates a changing magnetic field which induces an alternating potential difference across the secondary coil. If that secondary coil is connected in a circuit it will produce an alternating current.
- There are two types of transformer you should know:
- Step Up Transformer - A transformer which increase the potential difference.
- Step Down Transformer - A transformer which decrease the potential difference.
- Step up transformers are used in the National Grid to increase the potential difference and decrease the current for long distance transmission.
| This diagram of a transformer shows that an alternating current in the primary coil induces an alternating potential difference in the secondary coil. |
Equation
NB: You must be able to use this equation, but you do not need to remember it.
(Primary Potential Difference)/(Secondary Potential Difference)=(Primary Coils)/(Secondary Coils)
\(\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{n_p}{n_s}\)
\(V_p\) = The potential difference across the primary coil.
\(V_s\) = The potential difference across the secondary coil.
\(n_p\) = The number of loops on the primary coil.
\(n_s\) = The number of loops on the secondary coil.
Example Calculations
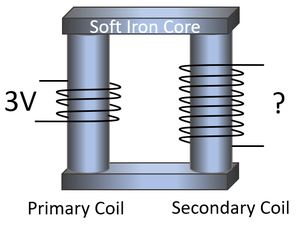
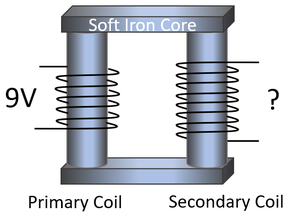
| Calculate the potential difference across the secondary coil. | Calculate the potential difference across the secondary coil. |
| 1. State the known quantities in SI Units.
\(V_p\) = 3V \(n_p\) = 4 coils \(n_s\) = 8 coils |
1. State the known quantities in SI Units.
\(V_p\) = 9V \(n_p\) = 6 coils \(n_s\) = 8 coils |
| 2. Substitute the numbers and evaluate.
\(\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{n_p}{n_s}\) \(\frac{3}{V_s} = \frac{4}{8}\) \(\frac{3}{V_s} = 0.5\) |
2. Substitute the numbers and evaluate.
\(\frac{V_p}{V_s} = \frac{n_p}{n_s}\) \(\frac{9}{V_s} = \frac{6}{8}\) \(\frac{9}{V_s} = 0.75\) |
| 3. Rearrange the equation and solve.
\(0.5 \times V_s = 3\) \(V_s = 6V\) |
3. Rearrange the equation and solve.
\(0.75 \times V_s = 9\) \(V_s = 12V\) |