Difference between revisions of "Litmus Paper"
(→About Litmus Paper) |
|||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
===About Litmus Paper=== | ===About Litmus Paper=== | ||
: '''Litmus paper''' comes in two colours: Red and Blue. | : '''Litmus paper''' comes in two colours: Red and Blue. | ||
| − | : '''Litmus paper''' is a very simple [[Indicator (Chemistry|indicator]] as it can only tell if something is [[acid]] or [[alkali]] but it cannot tell the exact [[pH]] of a [[solution]]. | + | : '''Litmus paper''' is a very simple [[Indicator (Chemistry)|indicator]] as it can only tell if something is [[acid]] or [[alkali]] but it cannot tell the exact [[pH]] of a [[solution]]. |
: '''Litmus paper''' cannot be used on a [[base]] unless it is in [[solution]]. | : '''Litmus paper''' cannot be used on a [[base]] unless it is in [[solution]]. | ||
Revision as of 12:19, 8 April 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning
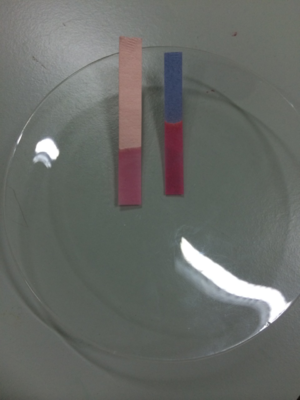
Two pieces of litmus paper dipped in an acid showing the red litmus stayed red but the blue litmus turned red.
Litmus paper is a piece of paper coloured with a dye that turns red in acid and blue in alkali.
About Litmus Paper
- Litmus paper comes in two colours: Red and Blue.
- Litmus paper is a very simple indicator as it can only tell if something is acid or alkali but it cannot tell the exact pH of a solution.
- Litmus paper cannot be used on a base unless it is in solution.
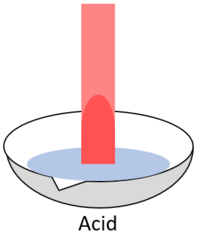
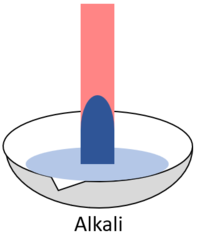
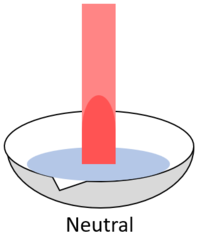
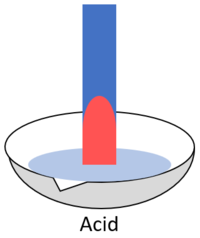
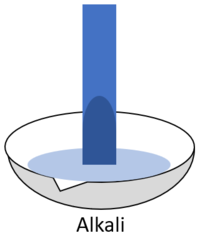
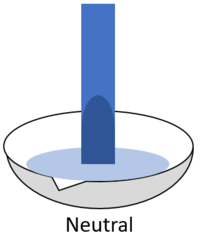
| When red litmus is placed in an acid it stays red. | When red litmus is placed in an alkali it turns blue. | When red litmus is placed in a neutral solution it stays red. |
| When blue litmus is placed in an acid it turns red. | When blue litmus is placed in an alkali it stays blue. | When blue litmus is placed in a neutral solution it stays blue. |