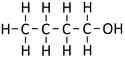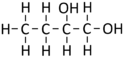Difference between revisions of "Butanol"
(→Butan-12-diol) |
|||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
: [[Butanol]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | : [[Butanol]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Carbon Dioxide]] + [[Water]] | ||
| − | ====Butan- | + | ====Butan-1,2-diol==== |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 07:21, 24 April 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Butanol is a compound with chemical formula C4H9OH.
About Butanol
- Butanol is a transparent liquid (at room temperature).
- Butanol can be oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Butanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Butanol is an alcohol molecule with chemical formula C4H9OH.
About Butanol
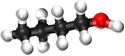
Butan-1-ol
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | Structural Formula | Structural Diagram | Ball and Stick Model |
| C4H9OH | CH3CH2CH2CH2OH |
- The combustion of Butanol produces Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Butanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>C4H9OH + 6O2 -> 4CO2 + 5H2O</chem>
- Butanol can also be oxidised at low temperatures to produce Water and the Carboxylic Acid; Butanoic Acid.
- <chem>C4H9OH + O2 -> C3H7COOH + H2O</chem>
- Butanol can be oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Butanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
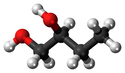
Butan-1,2-diol
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | Structural Formula | Structural Diagram | Ball and Stick Model |
| C4H8(OH)2 | CH3CH2CHOHCH2OH |
- The combustion of Butandiol produces Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Butandiol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
- <chem>2C4H8(OH)2 + 11O2 -> 8CO2 + 10H2O</chem>