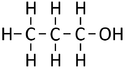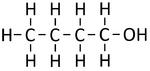Alcohol
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Alcohol is a legal drug sold as a drink.
About Alcohol
- Alcohol has intoxicating effects on humans, causing them to behave in ways they wouldn't normally when sober.
- Alcohol is toxic in large quantities and over long periods of time.
- Alcohol poisoning can cause a person to die if too much alcohol is consumed in a short period of time. However, usually people do not die directly from the alcohol but because they drown in their own vomit or become involved in an accident.
- Prolonged alcohol abuse can lead to liver and kidney damage and even failure. This may require a liver transplant or a kidney transplant.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
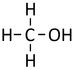
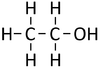
Alcohols are organic compounds containing an OH group attached to a Carbon chain and the general formula; CnH2n+1OH. The term alcohol may also be used to refer to one particular type of alcohol called ethanol which is used as a drug.
About Alcohol Molecules
- Alcohols are a homologous series of organic compounds.
- The functional group of the Alcohols is the OH group attached to a Carbon atom.
- Alcohols are long chains of Carbon atoms covalently bonded together with single bonds, an OH group attached to a Carbon atom and Hydrogen atoms taking the remaining bonds.
There are several alcohol molecules you should know:
Examples
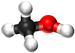
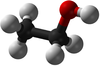
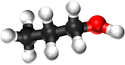
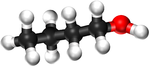
| Methanol | Ethanol | Propanol | Butanol | |
| Chemical Formula (CnH2n+2) | CH3OH | C2H5OH | C3H7OH | C4H9OH |
| Structural Formula | CH3OH | CH3CH2OH | CH3CH2CH2OH | CH3CH2CH2CH2OH |
| Structural Diagram | ||||
| Ball and Stick Model |
Reactions of Alcohols
Combustion
During combustion of alcohols the Carbon and Hydrogen atoms are oxidised to produce Carbon Dioxide and Water.
Complete Combustion
Complete combustion occurs when there is enough Oxygen to completely Oxidise all of the atoms in the alcohol. In the complete combustion of alcohols the only products are Carbon Dioxide and Water.
- Methanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(2CH_3OH + 3O_2 → 2CO_2 + 4H_2O\)
- Ethanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(C_2H_5OH + 3O_2 → 2CO_2 + 3H_2O\)
- Propanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(2C_3H_7OH + 9O_2 → 6CO_2 + 8H_2O\)
- Butanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(C_4H_9OH + 6O_2 → 4CO_2 + 5H_2O\)
Incomplete Combustion
Incomplete combustion occurs when there is not enough Oxygen to Oxidise all of the atoms in the alcohol. During incomplete combustion of alcohols the products may include Carbon (soot) and Carbon Monoxide.
\(2CH_3OH + O_2 → 2C + 4H_2O\)
- Methanol + Oxygen → Carbon Monoxide + Water
\(CH_3OH + O_2 → CO + 2H_2O\)
\(C_2H_5OH + O_2 → 2C + 3H_2O\)
- Ethanol + Oxygen → Carbon Monoxide + Water
\(C_2H_5OH + 2O_2 → 2CO + 3H_2O\)
- Ethanol + Oxygen → Soot + Carbon Monoxide + Water
\(2C_2H_5OH + 3O_2 → 2C + 2CO + 6H_2O\)
Reaction with Sodium
Sodium reacts with alcohol to produce Hydrogen gas.
\(2CH_3OH + 2Na → 2CH_3ONa + H_2\)
\(2C_2H_5OH + 2Na → 2C_2H_5ONa + H_2\)
\(2C_3H_7OH + 2Na → 2C_2H_5ONa + H_2\)
\(2C_4H_9OH + 2Na → 2C_2H_5ONa + H_2\)
Oxidation
When alcohols are oxidised without combustion they produce Carboxylic Acids.
- Methanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(CH_3OH + O_2 → HCOOH + H_2O\)
- Ethanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(C_2H_5OH + O_2 → CH_3COOH + H_2O\)
- Propanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(C_3H_7OH + O_2 → C_2H_5COOH + H_2O\)
- Butanol + Oxygen → Carbon Dioxide + Water
\(C_4H_9OH + O_2 → C_3H_7COOH + H_2O\)
Esterification
Alcohols may react with Carboxylic Acids to produce compounds known as esters which have the functional group -COO-.
- Methanol + Ethanoic Acid → Methyl Ethanoate + Water
\(CH_3OH + CH_3COOH → CH_3COOCH_3 + H_2O\)
- Ethanol + Ethanoic Acid → Ethyl Ethanoate + Water
\(C_2H_5OH + CH_3COOH → CH_3COOC_2H_5 + H_2O\)
- Propanol + Propanoic Acid → Propyl Propanoate + Water
\(C_3H_7OH + C_2H_5COOH → C_2H_5COOC_3H_7 + H_2O\)
- Butanol + Propanoic Acid → Butyl Propanoate + Water
\(C_4H_9OH + C_2H_5COOH → C_2H_5COOC_4H_9 + H_2O\)
References
AQA
- Alcohols, page 181, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Alcohols, pages 159-163, 170-171, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Alcohols, pages 226-7, 242-3, 245, 248-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Alcohols, pages 234, 238-240, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Alcohols, pages 79, 81, 82, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Alcohols; comparing alcohol fuels 187, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Alcohols; reactions of, pages 181-2, 184, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Alcohols; uses of, page 183, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Alcohols, page 291, 299-306, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Alcohols, pages 100, 102-104, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Alcohols, pages 178-179, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Alcohols; as fuels, page 104, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Alcohols; combustion of, page 303, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Alcohols; ethanol, pages 176-177, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel