Difference between revisions of "Bond Energy"
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
Once the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] is complete 97kJ will be released. | Once the [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] is complete 97kJ will be released. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d62 ''Bond energies, page 63, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Bond energies, pages 133-5, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294639X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294639X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=51599bb45a2bfaf7c1b6a978b2ca2616 ''Bond energies, pages 158, 159, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Bond energies, pages 183, 184, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Bond energies, pages 235-7, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Bond energy, pages 117-119, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 12:04, 28 October 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4 Higher
Meaning
Bond Energy is the energy needed to break a chemical bond between two atoms.
About Bond Energy
- When chemical bonds are formed energy is released to the surroundings increasing the temperature. An exothermic process]].
- To break chemical bonds energy is needed to separate the atoms, decreasing the temperature of the surroundings. An endothermic process]].
Examples
Some common bond energies are given in the table below.
| Bond | Energy in kJ/mol |
| H-H | 436 |
| O=O | 498 |
| N≡N | 941 |
| C-C | 347 |
| C=C | 614 |
| C≡C | 839 |
| C-H | 413 |
| O-H | 464 |
| C=O | 799 |
| Cl-Cl | 243 |
| H-Cl | 432 |
| N-H | 391 |
These can be used to calculate the energy released per mole in a chemical reaction.
Example 1
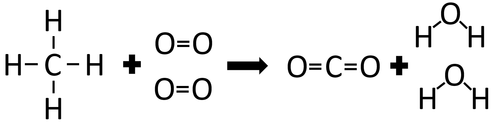
| In the reaction between Methane and Oxygen the chemical bonds in the reactants must be broken first before the bonds in the products are formed. |
There are 4 C-H bonds and 2 O=O bonds.
4 x 413 + 2 x 498 = 2648kJ
Therefore 2648kJ/mol are needed to break the bonds in the reactants.
There are 2 C=O bonds and 4 O-H bonds.
2 x 799 + 4 x 464 = 3454kJ
Therefore 3454kJ/mol is released when the bonds in the products form.
Once the reaction is complete 806kJ will be released.
Example 2
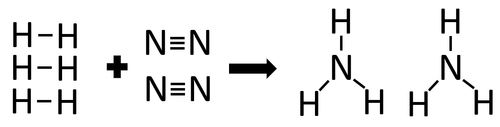
| In the reaction between Hydrogen and Nitrogen the chemical bonds in the reactants must be broken first before the bonds in the products are formed. |
There are 3 H-H bonds and 1 N≡N bonds.
3 x 436 + 1 x 941 = 2249kJ
Therefore 2249kJ/mol are needed to break the bonds in the reactants.
There are 6 N-H bonds.
6 x 391 = 2346kJ
Therefore 2346kJ/mol is released when the bonds in the products form.
Once the reaction is complete 97kJ will be released.
References
AQA
- Bond energies, page 63, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Bond energies, pages 133-5, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Bond energies, pages 158, 159, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Bond energies, pages 183, 184, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Bond energies, pages 235-7, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Bond energy, pages 117-119, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA