Difference between pages "Measure" and "GCSE Physics Required Practical: Calculating Densities"
(Difference between pages) (→Key Stage 2) |
(→Improving Precision) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | ==Key Stage | + | ==Key Stage 4== |
| + | {{#ev:youtube|https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lvqu6JAbaKc}} | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | + | Finding the [[density]] of [[solid]] [[object]]s. | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | ===Experiment 1: Cuboid=== |
| − | === | + | ====Method==== |
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:RequiredPracticalDensity1.png|center|400px]] | ||
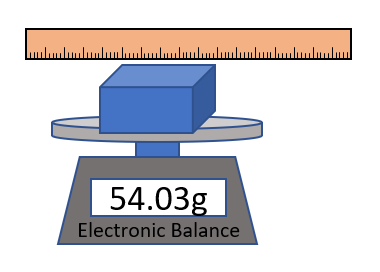
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of the [[apparatus]] used in an [[experiment]] to find the [[density]] of a cuboid. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | #Measure the [[mass]] of the cuboid using an [[Electronic Balance|electronic balance]] or [[Measuring Scale|measuring scale]]. | |
| − | + | #Measure the length, width and height of the cuboid using a [[ruler]]. | |
| − | + | #Multiply the length, width and height to calculate the [[Volume (Space)|volume]]. | |
| + | #Use the equation <math>\rho = \frac{m}{V}</math> to calculate the [[density]] of the cuboid. | ||
| − | == | + | ====Improving [[Accuracy]]==== |
| − | = | + | : Place the [[Electronic Balance|electronic balance]] on a flat, level surface to get an [[accurate]] reading of the [[mass]]. |
| − | |||
| − | === | + | ===Experiment 1: Irregular Solid=== |
| − | + | ====Method==== | |
| − | : | + | {| class="wikitable" |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:RequiredPracticalDensity2.png|center|600px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
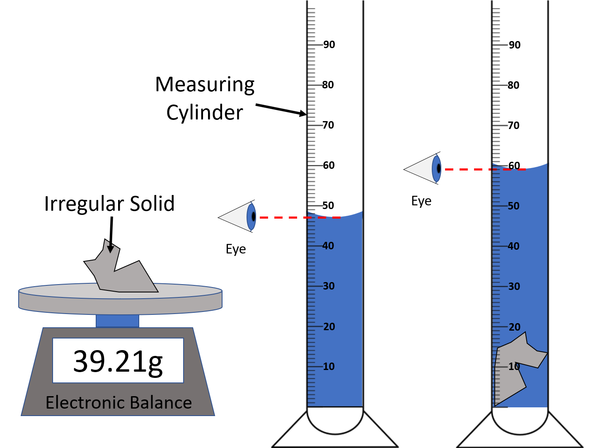
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] of the [[apparatus]] used in an [[experiment]] to find the [[density]] of an irregular [[solid]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| − | + | #Measure the [[mass]] of the [[object]] using an [[Electronic Balance|electronic balance]] or [[Measuring Scale|measuring scale]]. | |
| − | + | #Fill a [[Measuring Cylinder|measuring cylinder]] with enough [[water]] to submerse the [[object]]. | |
| − | + | #Take a [[reading]] of the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[water]] in the [[Measuring Cylinder]]. | |
| + | #Place the [[object]] in the [[Measuring Cylinder]] and ensure it is submersed. | ||
| + | #Take a [[reading]] of the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[water]] + [[object]] in the [[Measuring Cylinder]]. | ||
| + | #Subtract the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[water]] from the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[water]] + [[object]] to find the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of the [[object]]. | ||
| + | #Use the equation <math>\rho = \frac{m}{V}</math> to calculate the [[density]] of the irregular [[object]]. | ||
| − | === | + | ====Improving [[Accuracy]]==== |
| − | : | + | : Ensure the [[mass]] is [[measure]]d at the start of the [[experiment]] so that the [[mass]] is [[measure]]d while the [[object]] is dry. |
| − | : | + | : Place the [[Electronic Balance|electronic balance]] on a flat, level surface to get an [[accurate]] reading of the [[mass]]. |
| + | : Place the [[Measuring Cylinder|measuring cylinder]] on a flat, level surface and read it from eye level to get an [[accurate]] reading of the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of [[water]]. | ||
| + | : Ensure no [[water]] is spilled to get an accurate measurement for the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of the [[object]]. | ||
| + | : Ensure the [[object]] is fully submerged to get the correct value for the [[Volume (Space)|volume]] of the [[object]]. | ||
| − | === | + | ====Improving [[Precision]]==== |
| − | : | + | : Ensure no [[water]] is spilled from the [[Measuring Cylinder|measuring cylinder]] so that all repeat readings are the same. |
| + | : Measure the 'dry' [[mass]] of the [[object]] to ensure repeat readings are not affected by [[water]] permeating the [[object]]. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:19, 23 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Finding the density of solid objects.
Experiment 1: Cuboid
Method
| A diagram of the apparatus used in an experiment to find the density of a cuboid. |
- Measure the mass of the cuboid using an electronic balance or measuring scale.
- Measure the length, width and height of the cuboid using a ruler.
- Multiply the length, width and height to calculate the volume.
- Use the equation \(\rho = \frac{m}{V}\) to calculate the density of the cuboid.
Improving Accuracy
- Place the electronic balance on a flat, level surface to get an accurate reading of the mass.
Experiment 1: Irregular Solid
Method
| A diagram of the apparatus used in an experiment to find the density of an irregular solid. |
- Measure the mass of the object using an electronic balance or measuring scale.
- Fill a measuring cylinder with enough water to submerse the object.
- Take a reading of the volume of water in the Measuring Cylinder.
- Place the object in the Measuring Cylinder and ensure it is submersed.
- Take a reading of the volume of water + object in the Measuring Cylinder.
- Subtract the volume of water from the volume of water + object to find the volume of the object.
- Use the equation \(\rho = \frac{m}{V}\) to calculate the density of the irregular object.
Improving Accuracy
- Ensure the mass is measured at the start of the experiment so that the mass is measured while the object is dry.
- Place the electronic balance on a flat, level surface to get an accurate reading of the mass.
- Place the measuring cylinder on a flat, level surface and read it from eye level to get an accurate reading of the volume of water.
- Ensure no water is spilled to get an accurate measurement for the volume of the object.
- Ensure the object is fully submerged to get the correct value for the volume of the object.