Difference between revisions of "Alternating Current"
| (8 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Alternating currents, page 214, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Alternating currents, page 214, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 5== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Alternating Current]] ([[Alternating Current|AC]]) is an [[Electrical Current|electric current]] that periodically reverses direction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Alternating Currents=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Standard form of [[electricity]] supplied to homes and businesses. | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current|AC]] voltage oscillates in a sinusoidal pattern. | ||
| + | *Frequency of [[Alternating Current|AC]] is 50 [[Hertz|Hz]] or 60 [[Hertz|Hz]] depending on the region. | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current|Alternating current]] is used for power distribution because it is more efficient over long distances. | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current|AC]] can be easily transformed to different voltages using [[Electrical Transformer|transformers]]. | ||
| + | *The root mean square (RMS) value of [[Alternating Current|AC]] voltage is used to express its effective value. | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current|Alternating current]] can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI), which needs to be managed in sensitive electronic equipment. | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current|Alternating current]] is generated by [[alternator]]s in power plants and is used in [[motor]]s, [[generator]]s, and various household appliances. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | *Household electrical outlets provide [[Alternating Current|AC]] power. | ||
| + | *[[Alternating Current|AC]] is used in power transmission over long distances due to reduced energy loss. | ||
Latest revision as of 10:48, 19 May 2024
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An alternating current is an electrical current which changes direction.
About Alternating Currents
- Alternating currents are caused by alternating potential differences.
- Alternating currents have a frequency at which they alternate.
- Mains electricity is an alternating current working at a frequency of 50Hz, so the current changes direction 50 times every second.
- Alternating currents cannot be used to charge a cell or battery.
- Alternating currents cannot be used in electrolysis.
- Alternating currents are used in transformers.
Examples
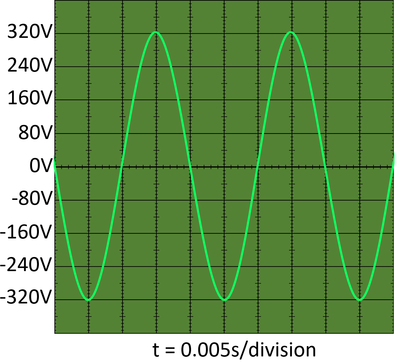
| An oscilloscope trace of mains electricity shows its frequency is 50Hz as the time period is 0.02s per oscillation and the peak potential difference is 320V, but the average over time is 230V. |
References
AQA
- Alternating current (a.c.), page 305, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA'
- Alternating current (a.c.), page 50, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA'
- Alternating current (a.c.), pages 46, 66, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA'
- Alternating current, pages 64-65, 224-229, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA'
- Alternating currents (a.c), page 188, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Alternating currents (ac), pages 31, 96, 97, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA'
- Alternating currents (ac), pages 86, 203, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA'
- Alternating currents (ac), pages 89, 245, 306, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA'
Edexcel
- Alternating current (a.c.), pages 397, 411, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Alternating current (a.c), pages 157, 174, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Alternating currents, page 246, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Alternating currents, pages 169, 192, 199, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Alternating currents, pages 45, 79, 89, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
Key Stage 5
Meaning
Alternating Current (AC) is an electric current that periodically reverses direction.
About Alternating Currents
- Standard form of electricity supplied to homes and businesses.
- AC voltage oscillates in a sinusoidal pattern.
- Frequency of AC is 50 Hz or 60 Hz depending on the region.
- Alternating current is used for power distribution because it is more efficient over long distances.
- AC can be easily transformed to different voltages using transformers.
- The root mean square (RMS) value of AC voltage is used to express its effective value.
- Alternating current can cause electromagnetic interference (EMI), which needs to be managed in sensitive electronic equipment.
- Alternating current is generated by alternators in power plants and is used in motors, generators, and various household appliances.