Difference between revisions of "Conservation of Mass"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
|[[File:ConservationofMassDissolving.png|center|400px]] | |[[File:ConservationofMassDissolving.png|center|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |Mass<sub>solvent</sub> + Mass<sub>solute</sub> = Mass<sub>solution</sub> | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Mass'''<sub>solvent</sub> + '''Mass'''<sub>solute</sub> = '''Mass'''<sub>solution</sub> |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 27 September 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Conservation of Mass is a law of the universe that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be moved from one place to another.
About Conservation of Mass
- In dissolving conservation of mass means that the mass of the solvent and the mass of the solute can be added to find the mass of the solution.
| Masssolvent + Masssolute = Masssolution |
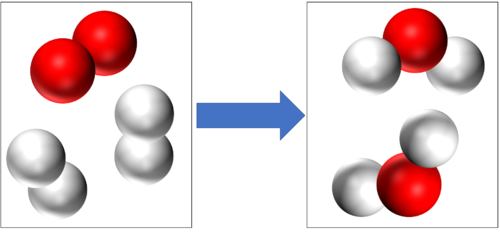
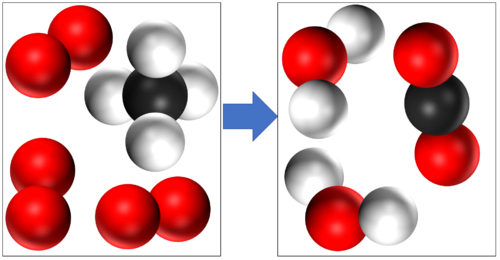
- In a chemical reaction conservation of mass means that the same atoms with made up the reactants must make up the products. So the atoms are not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, they are just rearranged.
|
Conservation of mass tells us that if there are 4 Hydrogen atoms and 2 Oxygen atoms at the start of this reaction then there will be the end of the reaction 4 Hydrogen atoms and 2 Oxygen atoms at the end of the reaction. |
|
In this reaction you can see that mass is conserved because there are 4 Hydrogen atoms, 4 Oxygen atoms and 1 Carbon atom in the reactants and all the same atoms are found in the products. |