Difference between revisions of "Exothermic"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File: | + | |[[File:ExothermicSketchGraphKS3.png|center|200px]] |
|- | |- | ||
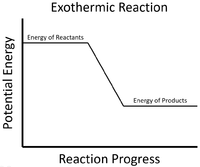
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[energy]] stored in the [[reactant]]s is released in the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] making the [[material]] increase in [[temperature]]. The [[product]]s now have less [[energy]] than the [[reactant]]s. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[energy]] stored in the [[reactant]]s is released in the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] making the [[material]] increase in [[temperature]]. The [[product]]s now have less [[energy]] than the [[reactant]]s. | ||
|} | |} | ||
: [[Freezing]], [[Condensing]] and [[Depositing]] are [[exothermic]] changes because it releases [[energy]] when it happens. The [[material]] has less after it has happened. However, there is usually no increase in [[temperature]] because the [[material]] is being cooled to [[State Change|change state]]. | : [[Freezing]], [[Condensing]] and [[Depositing]] are [[exothermic]] changes because it releases [[energy]] when it happens. The [[material]] has less after it has happened. However, there is usually no increase in [[temperature]] because the [[material]] is being cooled to [[State Change|change state]]. | ||
Revision as of 18:07, 29 September 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An exothermic process is one that gives out energy. This usually causes surroundings to increase in temperature.
About Exothermic Processes
- Most chemical reactions are exothermic with means they release energy to the environment and this is observed by an increase in temperature.
| The energy stored in the reactants is released in the chemical reaction making the material increase in temperature. The products now have less energy than the reactants. |
- Freezing, Condensing and Depositing are exothermic changes because it releases energy when it happens. The material has less after it has happened. However, there is usually no increase in temperature because the material is being cooled to change state.