Difference between revisions of "Convection"
(→Examples=) |
(→Examples in the Particle Model) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:ParticleConvectionHeater.png|center| | + | |[[File:ParticleConvectionHeater.png|center|400px]] |
| − | |[[File:ParticleConvectionCooler.png|center| | + | |[[File:ParticleConvectionCooler.png|center|400px]] |
|- | |- | ||
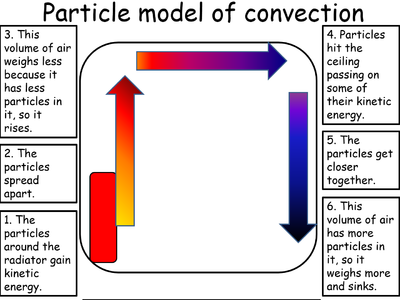
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:center;" |A [[Convection Current]] in the [[Particle Model|particle model]] caused by a heat source. |
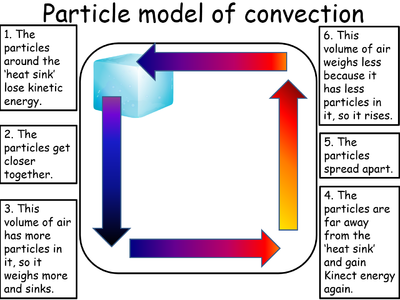
| − | | style="height:20px; width: | + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:center;" |A [[Convection Current]] in the [[Particle Model|particle model]] caused by a heat sink. |
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 08:29, 11 October 2018
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
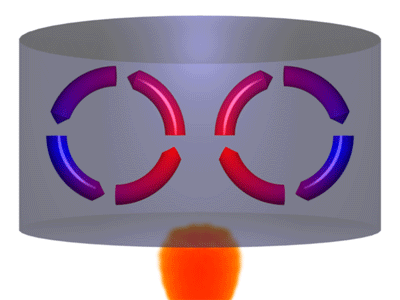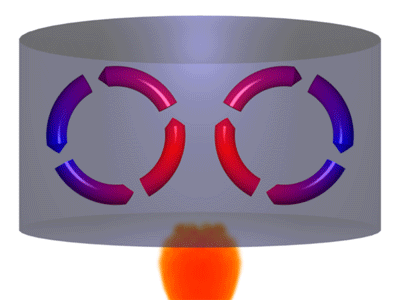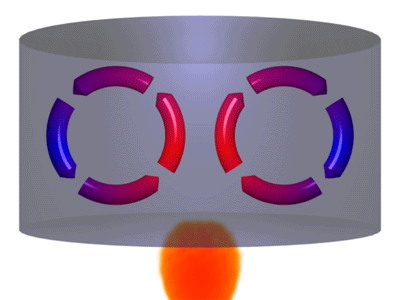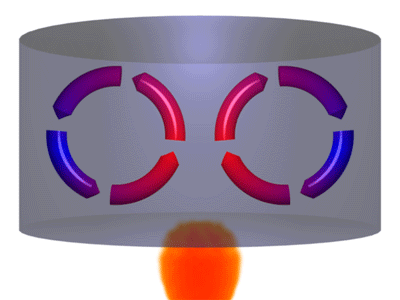
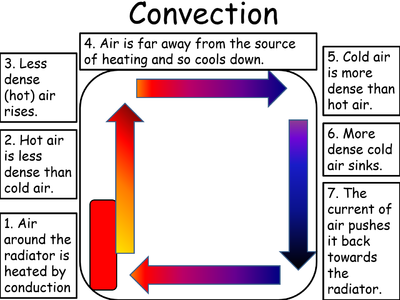
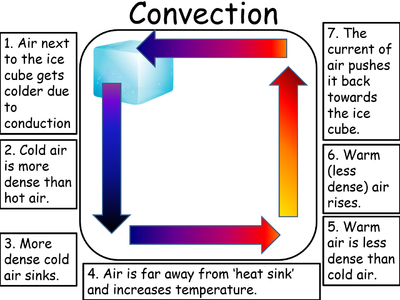
Convection is a process where thermal energy is transferred in a fluid due to particles moving from hotter regions to cooler regions.
About Convection
- Convection happens in fluids (liquids or gases) because particles can move past one another.
- When a fluid is heated particles move more quickly and spread further apart. This makes the fluid less dense. The less dense fluid rises. After the fluid has moved away from the heater it cools down, the particles move more slowly coming closer together. This makes the fluid more dense so it sinks back towards the heater.
Examples
| A Convection Current caused by a heat source. | A Convection Current caused by a heat sink. |
Examples in the Particle Model
| A Convection Current in the particle model caused by a heat source. | A Convection Current in the particle model caused by a heat sink. |