Difference between revisions of "Distance-Time Graph"
| Line 36: | Line 36: | ||
===Example Calculations=== | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:dtGraphCalculation1.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:dtGraphCalculation2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''Calculate the speed of the object in this 80 second journey.''' | ||
| + | : distance = 400[[m]] | ||
| + | : time = 80[[s]] | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{400}{80}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = 5m/s </math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''Calculate the speed of the object in the first 20 seconds.''' | ||
| + | : distance = 400[[m]] | ||
| + | : time = 20[[s]] | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{400}{20}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = 20m/s </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:dtGraphCalculation2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:dtGraphCalculation2.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''Calculate the speed of the object between 20 and 80 seconds''' | ||
| + | : distance = 100[[m]] | ||
| + | : time = 60[[s]] | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{100}{60}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = 1.7m/s </math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''Calculate the average speed of the object for its journey.''' | ||
| + | : distance = 500[[m]] | ||
| + | : time = 80[[s]] | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = {\tfrac{500}{80}} </math> | ||
| + | :<math>Speed = 6.25m/s </math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 08:52, 13 October 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A distance time graph is a graph that shows how the distance of an object from the origin changes with time.
About Distance Time Graphs
- Distance-time graphs give information about the journey taken by an object.
- On a distance time graph the distance is plotted on the y-axis and the time is plotted on the x-axis.
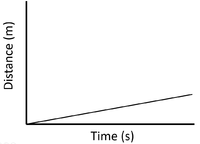
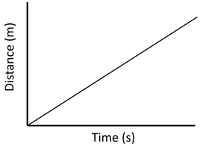
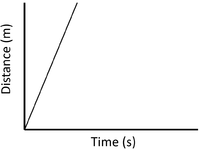
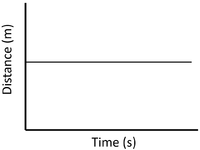
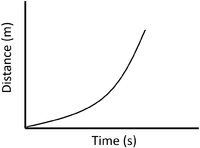
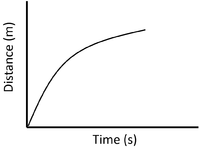
- A distance time graph can show the speed of an object.
| Slow Speed | Medium Speed | High Speed |
| A constant speed is shown by a constant positive gradient. | A higher gradient means a higher speed. | The highest speed is shown by the steepest gradient. |
| Stationary | Accelerating | Decelerating |
| A gradient of zero shows the object is not moving. | Acceleration is shown by an increasing gradient. | Deceleration is shown by a decreasing gradient. |
Example Calculations
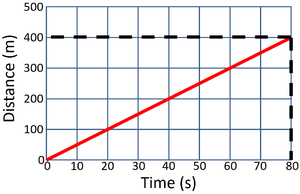
| Calculate the speed of the object in this 80 second journey.
\[Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} \] \[Speed = {\tfrac{400}{80}} \] \[Speed = 5m/s \] |
Calculate the speed of the object in the first 20 seconds.
\[Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} \] \[Speed = {\tfrac{400}{20}} \] \[Speed = 20m/s \] | |||
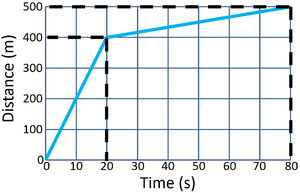
| Calculate the speed of the object between 20 and 80 seconds
\[Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} \] \[Speed = {\tfrac{100}{60}} \] \[Speed = 1.7m/s \] |
Calculate the average speed of the object for its journey.
\[Speed = {\tfrac{distance}{time}} \] \[Speed = {\tfrac{500}{80}} \] \[Speed = 6.25m/s \] |