Difference between revisions of "Air Resistance"
(→Examples) |
|||
| Line 83: | Line 83: | ||
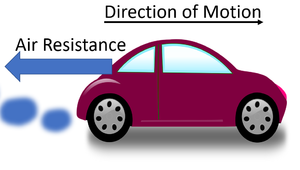
| style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A car engine must provide a constant [[force]] to stay at the same speed because the '''air resistance''' would cause it to slow down. | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A car engine must provide a constant [[force]] to stay at the same speed because the '''air resistance''' would cause it to slow down. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |[[File:AirResistanceTennisBall.png|center| | + | |[[File:AirResistanceTennisBall.png|center|100px]] |
|[[File:AirResistancePlane.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:AirResistancePlane.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 17:30, 14 October 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Air Resistance is a force that slows objects down when they are moving through the air.
- Noun: Air Resistance
About Air Resistance
- Air Resistance is a contact force.
- Air Resistance can only happen to an object surrounded by air. It does not happen to objects underwater or in space.
- The amount of air resistance depends on:
- The size of an object.
- The shape of an object.
- How fast an object is moving through the air.
| The van is smaller than the truck, so it feels less air resistance. | The truck is bigger than the van, so it feels more air resistance. |
| The scrunched up paper has a lot of air resistance and will slow down quickly when you throw it. | The paper plane is streamlined so it does not have much air resistance and will keep going fast once you've thrown it. |
| A spitfire can travel at a speed of 160 metres per second. | A jet fighter can travel 6 times faster that a spitfire so it feels a lot more air resistance. |
Experiments
Air Resistance and Weight
- Time how long it takes a single Cupcake case to fall from the ground from 1.5 metres high.
- Repeat this for two, three, four and five cupcake cases stacked together.
- This changes the weight without changing the shape of the object.
- If the difference is too small for meaningful results try 2, 4, 6, 8 and 10 cases.
- Plot the results on a Scatter Graph (not a line graph or bar chart).
Air Resistance and Shape
- Cut several different shaped parachutes from bin liners.
- Ensure that the surface area of all shapes is the same. This can support math skills calculating area of shapes.
- Use string to attach the parachutes to the same piece of plastacine each time.
- Plot the results on a Bar Chart (not a line graph or scatter graph).
Air Resistance and Size
- Cut several different size parachutes from bin liners.
- Ensure that the surface area of each parachute increases by the same amount each time. This can support math skills calculating area of shapes.
- Use string to attach the parachutes to the same piece of plastacine each time.
- Plot the results on a Scatter Graph (not a line graph or bar chart).
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Air Resistance is a force which acts to decelerate objects that are moving through the air.
About Air Resistance
- Air resistance is a contact force because it can only exist when an object is moving in the air.
- Air resistance increases with speed. The faster you travel the greater the air resistance.
- Air resistance depends on the surface area facing the direction of motion. The bigger the surface area, the larger the air resistance
Examples
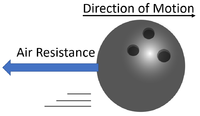
| As the bowling ball moves through the air the air resistance slows it down. | A car engine must provide a constant force to stay at the same speed because the air resistance would cause it to slow down. |
| On Earth the air resistance causes a tennis ball to have a terminal velocity as it falls but on The Moon there would be no air resistance because there is no air. | If the plane engine cuts out the air resistance will cause it to decelerate. |