Difference between revisions of "Parallel Circuit"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|- | |- | ||
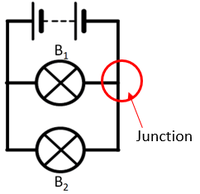
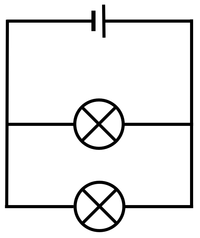
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Electrical Current|current]] from the [[battery]] splits at the [[junction]] sharing the [[Electrical Current|current]] between the two [[Electrical Bulb|bulbs]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Electrical Current|current]] from the [[battery]] splits at the [[junction]] sharing the [[Electrical Current|current]] between the two [[Electrical Bulb|bulbs]]. | ||
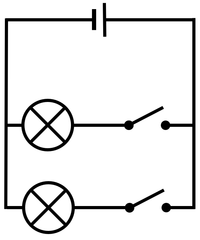
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The two [[Electrical Bulb|bulbs]] can be switched on and off separately. | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The two [[Electrical Bulb|bulbs]] in this '''parallel circuit''' can be switched on and off separately. |
|} | |} | ||
: [[Electrical Component|Components]] placed in '''parallel''' with each other have the same [[Potential Difference]] across them. | : [[Electrical Component|Components]] placed in '''parallel''' with each other have the same [[Potential Difference]] across them. | ||
Revision as of 14:24, 31 October 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
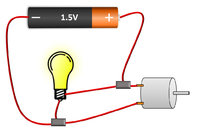
A Parallel Circuit is an electrical circuit with two or more paths the current can flow along.
About Parallel Circuits
- In a parallel circuit the current is split at junctions before taking a different path.
- Switches can be placed in a Parallel Circuit to allow current along one path at a time.
| The current from the battery splits at the junction sharing the current between the two bulbs. | The two bulbs in this parallel circuit can be switched on and off separately. |
- Components placed in parallel with each other have the same Potential Difference across them.
Examples
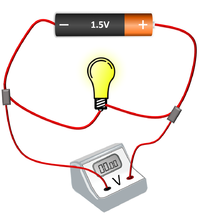
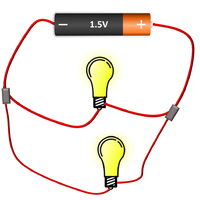
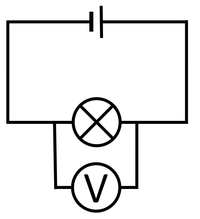
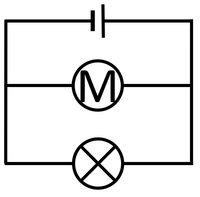
| The cell, bulb and Voltmeter are in parallel so they have the same Potential Difference across them. | The two bulbs are in parallel so they have the same Potential Difference across them but may have a different Current passing through them. | The bulb and motor are in parallel so they have the same Potential Difference across them but may have a different Current passing through them. |