Difference between revisions of "Bacteria"
(→About Bacteria) |
|||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
: [[Bacteria]] can cause disease but some are important to keep us healthy. | : [[Bacteria]] can cause disease but some are important to keep us healthy. | ||
: Some [[bacteria]] have a tail called a [[flagellum]] propel it move through [[water]]. | : Some [[bacteria]] have a tail called a [[flagellum]] propel it move through [[water]]. | ||
| − | : Some [[bacteria]] are encased in a [[Slime Capsule|slime capsule]] which protects them from some [[toxic]] [[chemical]]s. | + | : Some [[bacteria]] are encased in a [[Slime Capsule|slime capsule]] which protects them from [[phagocyte]]s and some [[toxic]] [[chemical]]s. |
: [[Bacteria]] do not have a [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]]. | : [[Bacteria]] do not have a [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]]. | ||
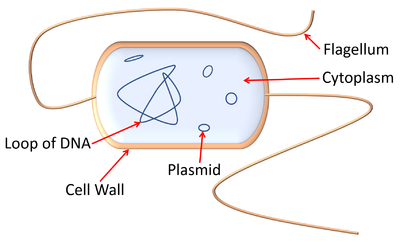
: The [[DNA]] of [[bacteria]] is in a loop. There are also smaller rings of [[DNA]] called [[plasmid]]s. | : The [[DNA]] of [[bacteria]] is in a loop. There are also smaller rings of [[DNA]] called [[plasmid]]s. | ||
Revision as of 21:10, 4 November 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A magnified image of several bacteria.
Bacteria are unicellular micro-organisms that have no nucleus, mitochondria or chloroplast but do have cytoplasm, a cell membrane and a cell wall.
About Bacteria
- Bacteria can cause disease but some are important to keep us healthy.
- Some bacteria have a tail called a flagellum.
- Bacteria do not have a nucleus.
- The DNA of bacteria is in a loop. There are also smaller rings of DNA called plasmids.
| A diagram showing the features of a bacterium. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Bacteria are unicellular prokaryotes (with no membrane bound organelles).
About Bacteria
- Bacteria can cause disease but some are important to keep us healthy.
- Some bacteria have a tail called a flagellum propel it move through water.
- Some bacteria are encased in a slime capsule which protects them from phagocytes and some toxic chemicals.
- Bacteria do not have a nucleus.
- The DNA of bacteria is in a loop. There are also smaller rings of DNA called plasmids.