Difference between revisions of "Mitosis"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | ''' | + | '''Mitosis''' is when a [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] splits into two smaller, identical, [[Cell (Biology)|cells]]. |
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Mitosis]] is the process of [[Asexual Reproduction|asexual reproduction]] where a parent [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] splits into two daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] that are [[genetically]] identical to the parent. | + | [[Mitosis]] is part of the [[Cell Cycle|cell cycle]] in which two identical [[Cell Nucleus|nuclei]] are formed and is followed by the [[Cell Division|cell division]] in which two identical [[Cell (Biology)cells]] are formed. |
| + | [[Mitosis]] may also refer to the process of [[Asexual Reproduction|asexual reproduction]] where a parent [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] splits into two daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] that are [[genetically]] identical to the parent. | ||
===About Mitosis=== | ===About Mitosis=== | ||
Revision as of 17:03, 8 November 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Mitosis is when a cell splits into two smaller, identical, cells.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
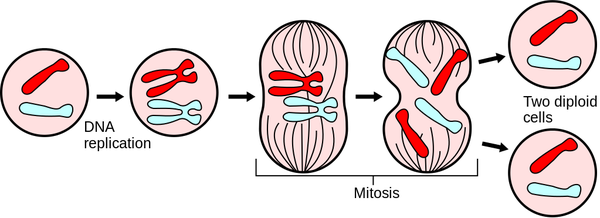
Mitosis is part of the cell cycle in which two identical nuclei are formed and is followed by the cell division in which two identical Cell (Biology)cells are formed. Mitosis may also refer to the process of asexual reproduction where a parent cell splits into two daughter cells that are genetically identical to the parent.
About Mitosis
- Mitosis is how unicellular organisms reproduce.
- Multicellular organisms grow by cells performing mitosis.
- The 2 daughter cells are genetically identical to each other.
- Before mitosis the cell spends its time copying the chromosomes.
- During mitosis the nucleus divides into two separate nuclei.
- The two daughter cells are called diploid cells because they contain chromosomes in matching pairs.
| A diagram showing the chromosomes during the process of mitosis. |