Difference between revisions of "Empirical Formula"
(→Finding the Empirical Formula) |
(→Finding the Empirical Formula) |
||
| Line 68: | Line 68: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |416g of [[Sulphur]] is found to [[Chemical Reaction|react]] completely with [[Oxygen]] to produce 832g of [[product]]. Find the '''empirical formula''' for the [[product]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |416g of [[Sulphur]] is found to [[Chemical Reaction|react]] completely with [[Oxygen]] to produce 832g of [[product]]. Find the '''empirical formula''' for the [[product]]. | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |State the [[mass]] of all [[reactant]]s. |
| − | State the [[mass]] of all [[reactant]]s. | ||
[[Mass]] of [[Oxygen]] = 64g | [[Mass]] of [[Oxygen]] = 64g | ||
| Line 75: | Line 74: | ||
[[Mass]] of [[Hydrogen]] = 8g | [[Mass]] of [[Hydrogen]] = 8g | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |State the [[mass]] of all [[reactant]]s. |
| − | State the [[mass]] of all [[reactant]]s. | ||
[[Mass]] of [[Carbon]] = 60g | [[Mass]] of [[Carbon]] = 60g | ||
| Line 82: | Line 80: | ||
[[Mass]] of [[Oxygen]] = 416g | [[Mass]] of [[Oxygen]] = 416g | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |State the [[mass]] of all [[reactant]]s. |
| − | State the [[mass]] of all [[reactant]]s. | ||
[[Mass]] of [[Sulphur]] = 416g | [[Mass]] of [[Sulphur]] = 416g | ||
| Line 91: | Line 88: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |Find the number of [[mole]]s of each [[element]]. |
| − | Find the number of [[mole]]s of each [[element]]. | ||
Number of [[Mole]]s = ([[Mass]]/[[Relative Atomic Mass]]) | Number of [[Mole]]s = ([[Mass]]/[[Relative Atomic Mass]]) | ||
| Line 109: | Line 105: | ||
[[Mole]]s of [[Hydrogen]] = 8 mole | [[Mole]]s of [[Hydrogen]] = 8 mole | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |Find the number of [[mole]]s of each [[element]]. |
| − | Find the number of [[mole]]s of each [[element]]. | ||
Number of [[Mole]]s = ([[Mass]]/[[Relative Atomic Mass]]) | Number of [[Mole]]s = ([[Mass]]/[[Relative Atomic Mass]]) | ||
| Line 129: | Line 124: | ||
[[Mole]]s of [[Oxygen]] = 10 mole | [[Mole]]s of [[Oxygen]] = 10 mole | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |Find the number of [[mole]]s of each [[element]]. |
| − | Find the number of [[mole]]s of each [[element]]. | ||
Number of [[Mole]]s = ([[Mass]]/[[Relative Atomic Mass]]) | Number of [[Mole]]s = ([[Mass]]/[[Relative Atomic Mass]]) | ||
| Line 148: | Line 142: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |Find the [[Ratio]]: |
| − | Find the [[Ratio]]: | ||
[[Hydrogen]]:[[Oxygen]] | [[Hydrogen]]:[[Oxygen]] | ||
| Line 156: | Line 149: | ||
2:1 | 2:1 | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |Find the [[Ratio]]: |
| − | Find the [[Ratio]]: | ||
[[Carbon]]:[[Oxygen]] | [[Carbon]]:[[Oxygen]] | ||
| Line 164: | Line 156: | ||
1:2 | 1:2 | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |Find the [[Ratio]]: |
| − | Find the [[Ratio]]: | ||
[[Sulphur]]:[[Oxygen]] | [[Sulphur]]:[[Oxygen]] | ||
Revision as of 16:58, 2 January 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An empirical formula is the simplest ratio of the different types of atom in a compound.
About Empirical Formulae
The empirical formula of a compound may not be the same as the chemical formula:
- Ethane - Chemical Formula C2H6, Empirical Formula CH3
- Ethene - Chemical Formula C2H4, Empirical Formula CH2
- Propene - Chemical Formula C3H6, Empirical Formula CH2
- Glucose - Chemical Formula C6H12O6, Empirical Formula CH2O
- Lactic Acid - Chemical Formula C3H6O3, Empirical Formula CH2O
- Empirical formulae are calculated from the amount of atoms in a chemical reaction.
- The number of atoms can be found if you know the mass of different elements and the relative atomic mass of the elements in the reaction.
Finding the Empirical Formula
| Number of Atoms | Skeletal Diagram | Ball and Stick Model |
| 100 atoms of Hydrogen react completely with 50 atoms of Oxygen. | ||
|
The ratio of Hydrogen atoms to Oxygen atoms H:O 100:50 2:1 So the empirical formula is H2O |
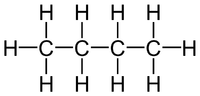
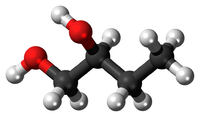
In this diagram there are 4 Carbon atoms, 10 Hydrogen atoms. C:H 4:10 2:5 So the empirical formula is C2H5 |
In this diagram there are 4 Carbon atoms, 10 Hydrogen atoms and 2 Oxygen atoms. C:H:O 4:10:2 2:5:1 So the empirical formula is C2H5O |
| 64g of Oxygen is found to react completely with 8g of Hydrogen. Find the empirical formula for the product. | 60g of Carbon is found to react completely with 160g of Oxygen. Find the empirical formula for the product. | 416g of Sulphur is found to react completely with Oxygen to produce 832g of product. Find the empirical formula for the product. |
| State the mass of all reactants. | State the mass of all reactants. | State the mass of all reactants.
|
| Find the number of moles of each element.
Number of Moles = (Mass/Relative Atomic Mass) Relative Atomic Mass of Oxygen = 16g
|
Find the number of moles of each element.
Number of Moles = (Mass/Relative Atomic Mass) Relative Atomic Mass of Carbon = 12g
|
Find the number of moles of each element.
Number of Moles = (Mass/Relative Atomic Mass) Relative Atomic Mass of Sulphur = 32g
|
| Find the Ratio:
8:4 2:1 |
Find the Ratio:
5:10 1:2 |
Find the Ratio:
13:26 1:2 |
| The empirical formula of the product is H2O | The empirical formula of the product is CO2 | The empirical formula of the product is SO2 |