Difference between revisions of "Acceleration"
(→Example Calculations) |
|||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
: u = initial [[speed]] | : u = initial [[speed]] | ||
: t = [[time]] | : t = [[time]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''A person starts at rest and accelerates to a [[speed]] of 8m/s in 0.8 [[second]]s. Calculate the acceleration of the person.''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''A racing car travels comes around a corner at a [[speed]] of 20m/s and in 1.5 [[second]]s accelerates to a [[speed]] of 80m/s. Calculate the acceleration of the racing car.''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | final speed = 8[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | initial speed = 0[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | time = 0.8[[s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{8-0}{0.8}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{8}{0.8}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = 10m/s/s </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | final speed = 80[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | initial speed = 20[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | time = 1.5[[s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{80-20}{1.5}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{60}{1.5}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = 40m/s/s </math> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''A [[horse]] begins trotting at 3.0m/s and accelerates to canter at 11m/s in 2.0 [[second]]s. Calculate the acceleration of the [[horse]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |'''A space probe is travelling at 18,000m/s and uses a thruster for 250 [[second]]s to slow down to 6,000m/s. Calculate the acceleration of the space probe.''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | final speed = 11[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | initial speed = 3.0[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | time = 2.0[[s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{11-3.0}{2.0}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{8.0}{2.0}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = 4m/s/s </math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | final speed = 18,000[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | initial speed = 6,000[[m/s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | time = 250[[s]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{18,000-6,000}{250}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{12,000}{250}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = 48m/s/s </math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Acceleration''' is a [[vector]] quantity that describes a change in [[velocity]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Acceleration=== | ||
| + | : [[Acceleration]] is a [[vector]] because it has a [[magnitude]] and direction. | ||
| + | : The [[SI Unit]]s of [[acceleration]] and metres per second per second (m/s/s). | ||
| + | [[Acceleration]] may refer to: | ||
| + | *Increasing [[speed]] - The [[magnitude]] of the [[velocity]] increases. | ||
| + | *Decreasing [[speed]] - The [[magnitude]] of the [[velocity]] decreases, also known as [[deceleration]]. | ||
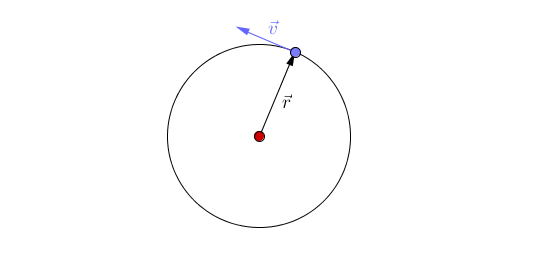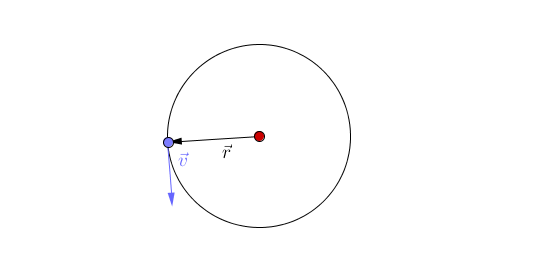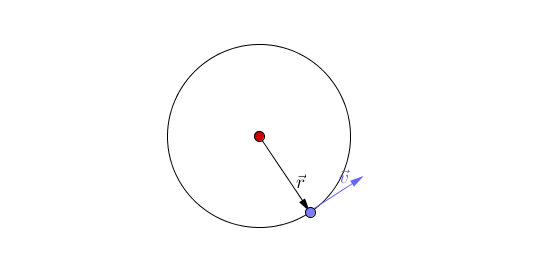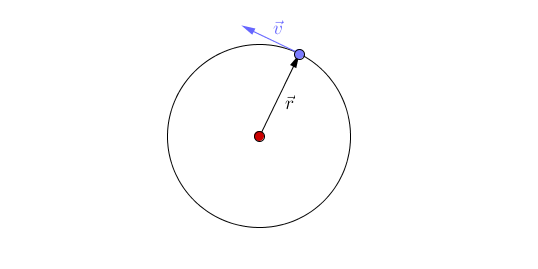
| + | *Changing direction - The [[magnitude]] of the [[velocity]] remains constant (constant [[speed]]) but the [[object]] changes direction of travel. | ||
| + | : [[Acceleration]] occurs due to [[Unbalanced Forces|unbalanced forces]] on an [[object]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
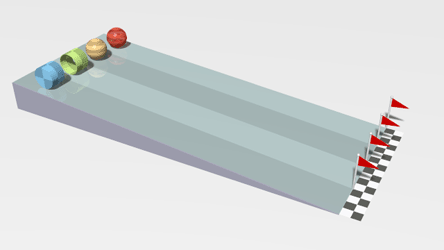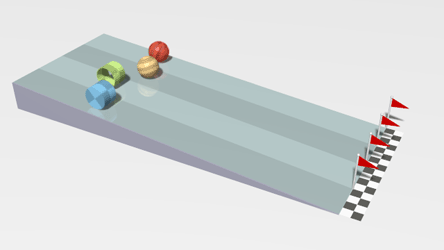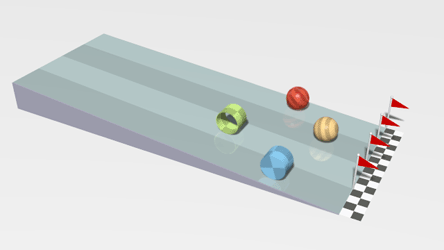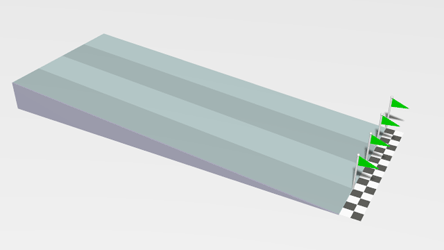
| + | |[[File:Rollers.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |[[File:CircularMotion.gif|center]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows a [[linear]] [[acceleration]] as the [[object]]s roll down the slope. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows [[acceleration]] due to a changing direction. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Equation=== | ||
| + | ====Acceleration, Velocity and time==== | ||
| + | ''NB: You must remember this equation.'' | ||
| + | |||
| + | This equation applies to [[linear]] [[acceleration]] but not to a change in direction. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a = {\tfrac{\delta v}{t}} </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where: | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>a</math> = [[Acceleration]] of the [[object]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>\delta v</math> = Change in [[magnitude]] of the [[velocity]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>t</math>= [[Time]] taken for the change in [[velocity]]. | ||
===Example Calculations=== | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
Revision as of 09:28, 13 February 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Acceleration is an increase in speed.
About Acceleration
- The opposite of acceleration is deceleration which is to slow down.
- Acceleration happens when an object experiences Unbalanced Forces.
Acceleration Equation
\[a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \] Where:
- a = acceleration
- v = final speed
- u = initial speed
- t = time
Example Calculations
| A person starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 8m/s in 0.8 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the person. | A racing car travels comes around a corner at a speed of 20m/s and in 1.5 seconds accelerates to a speed of 80m/s. Calculate the acceleration of the racing car. |
|
final speed = 8m/s initial speed = 0m/s time = 0.8s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{8-0}{0.8}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{8}{0.8}} \) \(a = 10m/s/s \) |
final speed = 80m/s initial speed = 20m/s time = 1.5s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{80-20}{1.5}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{60}{1.5}} \) \(a = 40m/s/s \) |
| A horse begins trotting at 3.0m/s and accelerates to canter at 11m/s in 2.0 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the horse. | A space probe is travelling at 18,000m/s and uses a thruster for 250 seconds to slow down to 6,000m/s. Calculate the acceleration of the space probe. |
|
final speed = 11m/s initial speed = 3.0m/s time = 2.0s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{11-3.0}{2.0}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{8.0}{2.0}} \) \(a = 4m/s/s \) |
final speed = 18,000m/s initial speed = 6,000m/s time = 250s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{18,000-6,000}{250}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{12,000}{250}} \) \(a = 48m/s/s \) |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Acceleration is a vector quantity that describes a change in velocity.
About Acceleration
- Acceleration is a vector because it has a magnitude and direction.
- The SI Units of acceleration and metres per second per second (m/s/s).
Acceleration may refer to:
- Increasing speed - The magnitude of the velocity increases.
- Decreasing speed - The magnitude of the velocity decreases, also known as deceleration.
- Changing direction - The magnitude of the velocity remains constant (constant speed) but the object changes direction of travel.
- Acceleration occurs due to unbalanced forces on an object.
Examples
| This animation shows a linear acceleration as the objects roll down the slope. | This animation shows acceleration due to a changing direction. |
Equation
Acceleration, Velocity and time
NB: You must remember this equation.
This equation applies to linear acceleration but not to a change in direction.
\(a = {\tfrac{\delta v}{t}} \)
Where\[a\] = Acceleration of the object.
\(\delta v\) = Change in magnitude of the velocity.
\(t\)= Time taken for the change in velocity.
Example Calculations
| A person starts at rest and accelerates to a speed of 8m/s in 0.8 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the person. | A racing car travels comes around a corner at a speed of 20m/s and in 1.5 seconds accelerates to a speed of 80m/s. Calculate the acceleration of the racing car. |
|
final speed = 8m/s initial speed = 0m/s time = 0.8s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{8-0}{0.8}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{8}{0.8}} \) \(a = 10m/s/s \) |
final speed = 80m/s initial speed = 20m/s time = 1.5s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{80-20}{1.5}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{60}{1.5}} \) \(a = 40m/s/s \) |
| A horse begins trotting at 3.0m/s and accelerates to canter at 11m/s in 2.0 seconds. Calculate the acceleration of the horse. | A space probe is travelling at 18,000m/s and uses a thruster for 250 seconds to slow down to 6,000m/s. Calculate the acceleration of the space probe. |
|
final speed = 11m/s initial speed = 3.0m/s time = 2.0s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{11-3.0}{2.0}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{8.0}{2.0}} \) \(a = 4m/s/s \) |
final speed = 18,000m/s initial speed = 6,000m/s time = 250s \(a = {\tfrac{v-u}{t}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{18,000-6,000}{250}} \) \(a = {\tfrac{12,000}{250}} \) \(a = 48m/s/s \) |