Difference between revisions of "Motor Effect"
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|[[File:FlemingsLeftHandRule.png|center|300px]] | |[[File:FlemingsLeftHandRule.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MotorEffect.png|center|300px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align: | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | |
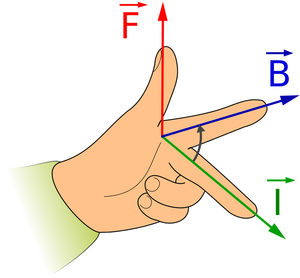
<math>\overrightarrow{B}</math>: First finger [[Magnetic Field|field]]. | <math>\overrightarrow{B}</math>: First finger [[Magnetic Field|field]]. | ||
| − | <math> | + | <math>{I}</math>: Second finger [[Electrical Current|current]]. |
<math>\overrightarrow{F}</math>: The [[force]]. | <math>\overrightarrow{F}</math>: The [[force]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" |The direction on the [[force]] on this [[wire]] can be found using [[Fleming's Left Hand Rule]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
<math>F = BIl</math> | <math>F = BIl</math> | ||
| − | Where | + | Where |
<math>B</math> = The [[Magnetic Flux Density]] (strength of [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]). | <math>B</math> = The [[Magnetic Flux Density]] (strength of [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]). | ||
| Line 39: | Line 41: | ||
===Example Calculations=== | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A [[wire]] carrying a [[Electrical Current|current]] of 2.3A is inside a 55mT [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]] that extends along the [[wire]] by a [[length]] of 6.1cm. Calculate the [[force]] on the [[wire]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |23cm of [[wire]] carrying 1.2A of [[Electrical Current|current]] is contained in a 37mT [[Magnetic Field|magnetic field]]. Calculate the [[force]] on the [[wire]] correct to two [[Significant Figures|significant figures]]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in [[SI Unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B</math> = 55mT = 55x10<sup>-3</sup>T | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I</math> = 2.3A | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>l</math> = 6.1cm = 6.1x10<sup>-2<sup>m | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''1. State the known quantities in [[SI Unit]]s.''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>B</math> = 37mT = 37x10<sup>-3</sup>T | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>I</math> = 1.2A | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>l</math> = 23cm = 23x10<sup>-2<sup>m | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = BIl</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = 55\times 10^{-3} \times 2.3 \times 6.1 \times 10^{-2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = 7.7165 \times 10^{-3}N</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F \approx 7.7\times 10^{-3}N</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:left;" |'''2. [[Substitute (Maths)|Substitute]] the numbers into the [[equation]] and [[Solve (Maths)|solve]].''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = BIl</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = 37\times 10^{-3} \times 1.2 \times 23 \times 10^{-2}</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F = 1.0212 \times 10^{-2}N</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>F \approx 1.0\times 10^{-2}N</math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Motor effect, page 228, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Motor effect, page 249, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Motor effect, pages 220-221, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Motor effect, pages 221-227, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Motor effect, pages 281, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Motor effect, pages 295-302, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac320 ''Motor effect, pages 94, 95, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Motor effect, page 172, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Motor effect, page 197, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Motor effect, page 406, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Motor effect, pages 273-278, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Motor effect, pages 87, 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:20, 22 January 2023
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
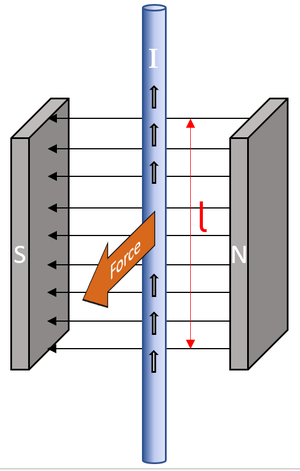
The motor effect is the force on a current carrying wire in a magnetic field.
About The Motor Effect
- When an a wire has an electrical current it has a magnetic field. If this wire is in the presence of an external magnetic field the two fields will interact causing a force.
- The magnitude of the force depends upon:
- The Current - The greater the current the greater the force.
- The Magnetic Field - The greater the strength of magnetic field the greater the force.
- The force on a current carrying wire is at right angles to both the current and the magnetic field.
- Fleming's Left Hand Rule can be used to find the direction of the force.
|
\(\overrightarrow{B}\): First finger field. \({I}\): Second finger current. \(\overrightarrow{F}\): The force. |
The direction on the force on this wire can be found using Fleming's Left Hand Rule. |
Equation
Force = (Magnetic Flux Density) x (Current) x (Length)
\(F = BIl\)
Where
\(B\) = The Magnetic Flux Density (strength of magnetic field).
\(I\) = The Electrical Current through the wire.
\(l\) = The length of wire inside the magnetic field.
\(F\) = The force on the wire.
Example Calculations
| A wire carrying a current of 2.3A is inside a 55mT magnetic field that extends along the wire by a length of 6.1cm. Calculate the force on the wire correct to two significant figures. | 23cm of wire carrying 1.2A of current is contained in a 37mT magnetic field. Calculate the force on the wire correct to two significant figures. |
| 1. State the known quantities in SI Units.
\(B\) = 55mT = 55x10-3T \(I\) = 2.3A \(l\) = 6.1cm = 6.1x10-2m |
1. State the known quantities in SI Units.
\(B\) = 37mT = 37x10-3T \(I\) = 1.2A \(l\) = 23cm = 23x10-2m |
| 2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(F = BIl\) \(F = 55\times 10^{-3} \times 2.3 \times 6.1 \times 10^{-2}\) \(F = 7.7165 \times 10^{-3}N\) \(F \approx 7.7\times 10^{-3}N\) |
2. Substitute the numbers into the equation and solve.
\(F = BIl\) \(F = 37\times 10^{-3} \times 1.2 \times 23 \times 10^{-2}\) \(F = 1.0212 \times 10^{-2}N\) \(F \approx 1.0\times 10^{-2}N\) |
References
AQA
- Motor effect, page 228, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Motor effect, page 249, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 220-221, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 221-227, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 281, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 295-302, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Motor effect, pages 94, 95, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Motor effect, page 172, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Motor effect, page 197, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Motor effect, page 406, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Motor effect, pages 273-278, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel
- Motor effect, pages 87, 88, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel