Difference between revisions of "Prism (Physics)"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Prism, page 226, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Prism, page 226, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Prisms, pages 26, 205, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Prisms, pages 26, 205, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Prisms, splitting of white light, pages 207-8, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Prisms, page 56, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Prisms, pages 164, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 16:31, 18 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
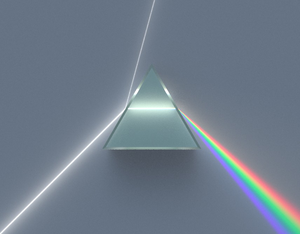
A prism is a transparent solid block with a triangular base.
About Prisms
- Prisms show how white light is made of many different colours.
- The different colours all refract by a different amount, causing them to split.
When white light enters a prism it is split into a spectrum of 7 colours:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
| A diagram of a prism showing how white light is made of the 7 colours of the spectrum. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
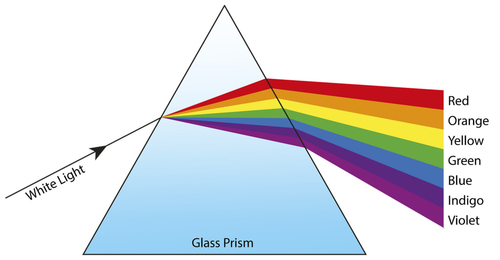
A prism is a transparent solid block with a triangular base.
About Prisms
- Prisms show how white light is made of many different colours.
- Prisms can be used in spectroscope to perform a chemical analysis.
- The different colours all refract by a different amount, causing them to split.
When white light enters a prism it is split into a spectrum of 7 colours:
- Red
- Orange
- Yellow
- Green
- Blue
- Indigo
- Violet
| A diagram of a prism showing how white light is made of the 7 colours of the spectrum. |
References
AQA
- Prism, page 226, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Prisms, pages 26, 205, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Prisms, splitting of white light, pages 207-8, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA