Difference between revisions of "Pathogenic Fungus"
| (3 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
: When a '''pathogenic fungus''' gets onto the body the [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] [[Cell Division|divides]] quickly making millions of copies of themselves. | : When a '''pathogenic fungus''' gets onto the body the [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] [[Cell Division|divides]] quickly making millions of copies of themselves. | ||
: '''Pathogenic fungus''' grows in warm, moist areas on the body. | : '''Pathogenic fungus''' grows in warm, moist areas on the body. | ||
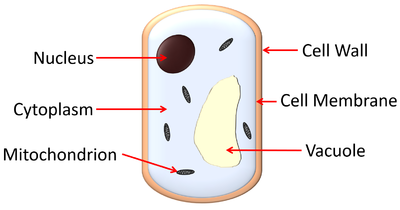
| − | : [[Fungi]] are [[Eukaryotic Cell|eukaryotes]] so they have a [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]] | + | : [[Fungi]] are [[Eukaryotic Cell|eukaryotes]] so they have a [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]] and [[mitochondria]]. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
| − | : | + | : Thrush is caused by a '''pathogenic fungus''' called [[Candida albicans|Candida ''albicans'']]. |
| − | : [[Rose Blackspot]] is a '''pathogenic fungus''' that affects | + | : [[Rose Blackspot]] is a '''pathogenic fungus''' that affects rose [[plant]]s. |
Latest revision as of 19:07, 3 April 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A pathogenic fungus is a fungus which causes disease.
About Pathogenic Fungus
- When a pathogenic fungus gets onto the body the cells divides quickly making millions of copies of themselves.
- Pathogenic fungus grows in warm, moist areas on the body.
- Fungi are eukaryotes so they have a nucleus and mitochondria.
| A diagram showing the features of a fungal cell. |
Examples
- Thrush is caused by a pathogenic fungus called Candida albicans.
- Rose Blackspot is a pathogenic fungus that affects rose plants.