Difference between revisions of "Meiosis"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
===About Meiosis=== | ===About Meiosis=== | ||
: [[Meiosis]] is how [[multicellular]] [[organism]]s (including [[human]]s) produce [[gamete]]s for [[Sexual Reproduction|sexual reproduction]]. | : [[Meiosis]] is how [[multicellular]] [[organism]]s (including [[human]]s) produce [[gamete]]s for [[Sexual Reproduction|sexual reproduction]]. | ||
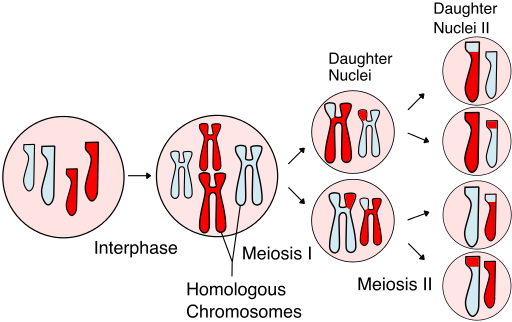
| − | : | + | : '''Meiotic [[Cell Division|cell division]]''' results in the production of 4 daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] which are all [[genetically]] different to each other. |
| − | : During [[ | + | : During '''meiotic [[Cell Division|cell division]]''' the [[Cell Nucleus|nucleus]] divides into two separate [[diploid]] [[Cell Nucleus|nuclei]] before dividing a second time to produce 4 [[haploid]] [[Cell Nucleus|nuclei]]. |
: The four daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] are called [[haploid]] [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] because they contain half the number [[chromosome]]s needed to grow a new [[organism]]. | : The four daughter [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] are called [[haploid]] [[Cell (Biology)|cells]] because they contain half the number [[chromosome]]s needed to grow a new [[organism]]. | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
Revision as of 11:57, 18 June 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Meiosis is the process of asexual reproduction where a parent cell produces four haploid daughter cells known as gametes that are all genetically unique.
Noun: Meiosis
Adjective: Meiotic
About Meiosis
- Meiosis is how multicellular organisms (including humans) produce gametes for sexual reproduction.
- Meiotic cell division results in the production of 4 daughter cells which are all genetically different to each other.
- During meiotic cell division the nucleus divides into two separate diploid nuclei before dividing a second time to produce 4 haploid nuclei.
- The four daughter cells are called haploid cells because they contain half the number chromosomes needed to grow a new organism.
| A diagram showing the chromosomes during the process of meiosis. |