Difference between revisions of "Conservation of Mass"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | [[Conservation of Mass]] is a law of the universe that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be moved from one place to another. | + | [[Conservation of Mass]] is a law of the universe that states that [[mass]] cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be moved from one place to another. |
===About Conservation of Mass=== | ===About Conservation of Mass=== | ||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | : In a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] '''conservation of mass''' means that the same [[atom]]s | + | : In a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] '''conservation of mass''' means that the same [[atom]]s which made up the [[reactant]]s must make up the [[product]]s. So the [[atom]]s are not created or destroyed in a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]], they are just rearranged. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
In this [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] you can see that '''mass is conserved''' because there are 4 [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s, 4 [[Oxygen]] [[atom]]s and 1 [[Carbon]] [[atom]] in the [[reactant]]s and all the same [[atom]]s are found in the [[product]]s. | In this [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] you can see that '''mass is conserved''' because there are 4 [[Hydrogen]] [[atom]]s, 4 [[Oxygen]] [[atom]]s and 1 [[Carbon]] [[atom]] in the [[reactant]]s and all the same [[atom]]s are found in the [[product]]s. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[Conservation of Mass]] is a law of the universe that states that [[mass]] cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be moved from one place to another. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Conservation of Mass=== | ||
| + | : In a [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reaction]] law of '''conservation of mass''' indicates that the total [[mass]] of the [[product]]s is the same as the total [[mass]] of the [[reactant]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | Methane + Oxygen → Water + Carbon Dioxide | ||
| + | CH<sub>4</sub> + 2O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O + CO<sub>2</sub> | ||
Revision as of 10:46, 3 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Conservation of Mass is a law of the universe that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be moved from one place to another.
About Conservation of Mass
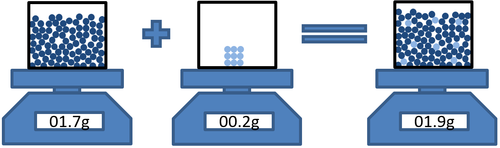
- In dissolving conservation of mass means that the mass of the solvent and the mass of the solute can be added to find the mass of the solution.
| Masssolvent + Masssolute = Masssolution |
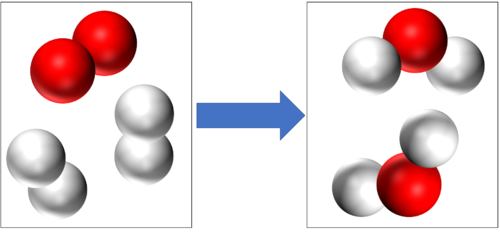
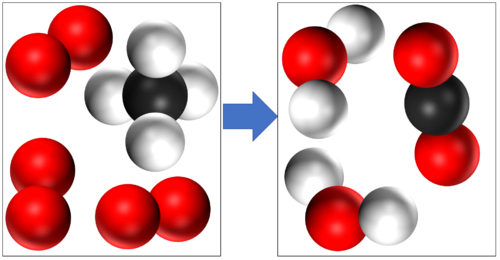
- In a chemical reaction conservation of mass means that the same atoms which made up the reactants must make up the products. So the atoms are not created or destroyed in a chemical reaction, they are just rearranged.
|
Conservation of mass tells us that if there are 4 Hydrogen atoms and 2 Oxygen atoms at the start of this reaction then there will be the end of the reaction 4 Hydrogen atoms and 2 Oxygen atoms at the end of the reaction. |
|
In this reaction you can see that mass is conserved because there are 4 Hydrogen atoms, 4 Oxygen atoms and 1 Carbon atom in the reactants and all the same atoms are found in the products. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Conservation of Mass is a law of the universe that states that mass cannot be created or destroyed, it can only be moved from one place to another.
About Conservation of Mass
- In a chemical reaction law of conservation of mass indicates that the total mass of the products is the same as the total mass of the reactants.
Examples
Methane + Oxygen → Water + Carbon Dioxide CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2