Difference between revisions of "Smelting"
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
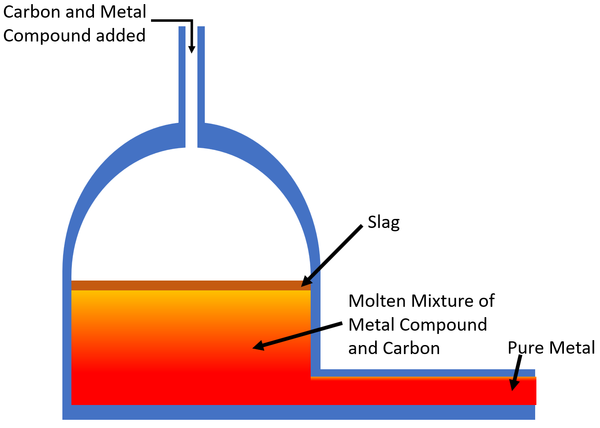
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Carbon]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] with the [[mineral]] in a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] creating usually producing [[Carbon Dioxide]] and the [[pure]] [[metal]] which is removed from the [[furnace]]. Any [[Impurity|impurities]] in the [[mineral]] rise to the top and make a layer called [[slag]] which is removed. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |The [[Carbon]] [[Chemical Reaction|reacts]] with the [[mineral]] in a [[Displacement Reaction|displacement reaction]] creating usually producing [[Carbon Dioxide]] and the [[pure]] [[metal]] which is removed from the [[furnace]]. Any [[Impurity|impurities]] in the [[mineral]] rise to the top and make a layer called [[slag]] which is removed. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Reactions=== | ||
| + | : Iron Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Iron | ||
| + | : Zinc Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc | ||
| + | : Tin Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Tin | ||
| + | : Lead Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Lead | ||
Revision as of 16:55, 1 October 2018
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Smelting is a process for extracting metals by heating and melting a mineral with carbon to cause a displacement reaction.
About Smelting
- Any metal below Carbon on the Reactivity Series can be extracted from its by smelting with Carbon.
- When the ore is melted it Carbon is added and a displacement reaction happens where the Carbon replaces the metal in the mineral.
| The Carbon reacts with the mineral in a displacement reaction creating usually producing Carbon Dioxide and the pure metal which is removed from the furnace. Any impurities in the mineral rise to the top and make a layer called slag which is removed. |
Example Reactions
- Iron Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Iron
- Zinc Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Zinc
- Tin Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Tin
- Lead Oxide + Carbon → Carbon Dioxide + Lead