Difference between revisions of "Thermal Conduction"
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===About Thermal Conduction=== | ===About Thermal Conduction=== | ||
: Of the three [[State of Matter|states of matter]], [[solid]]s are the best '''conductors''' of [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy]]. [[Solid]]s are better [[Thermal Conductor|thermal conductors]] because the [[particle]]s are touching one another allowing them to pass on their [[energy]] quickly. | : Of the three [[State of Matter|states of matter]], [[solid]]s are the best '''conductors''' of [[Thermal Energy Store|thermal energy]]. [[Solid]]s are better [[Thermal Conductor|thermal conductors]] because the [[particle]]s are touching one another allowing them to pass on their [[energy]] quickly. | ||
| − | : [[Metal]]s are better '''[[Thermal Conductor|thermal conductors]]''' than [[Non-metal|non-metals]] because [[metal]]s have [[ | + | : [[Metal]]s are better '''[[Thermal Conductor|thermal conductors]]''' than [[Non-metal|non-metals]] because [[metal]]s have [[Delocalised Electrons|free electrons]] that can pass along [[Thermal Energy|thermal energy]]. |
Revision as of 09:36, 8 April 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning
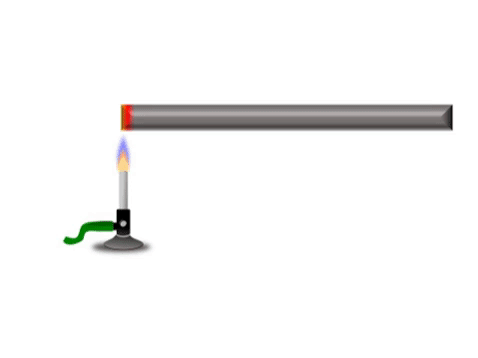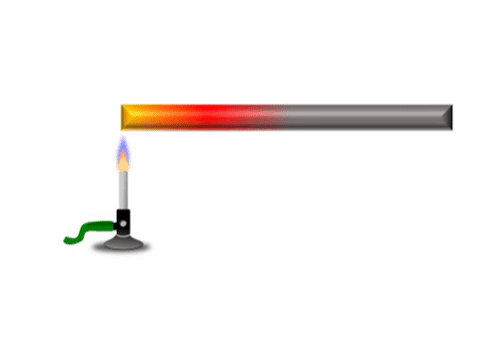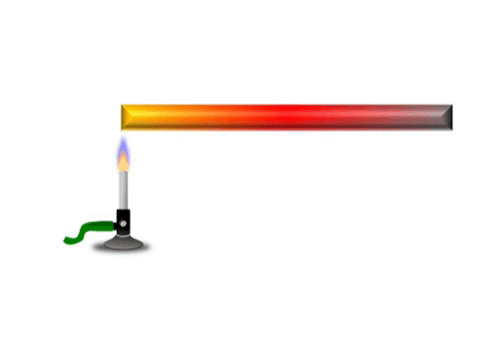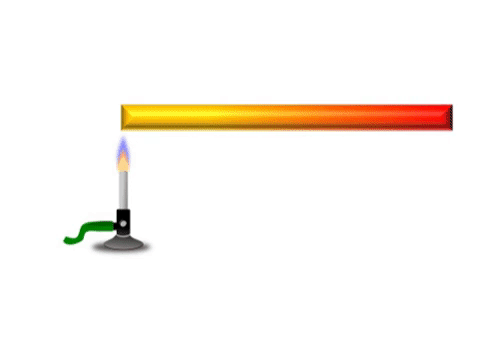
Conduction is when thermal energy passes along a material from the hotter region to the cooler region.
| Grey represents the metal bar at a cold temperature. The yellow represents the highest temperature and red represents a temperature between yellow and grey. |
About Thermal Conduction
- Of the three states of matter, solids are the best conductors of thermal energy. Solids are better thermal conductors because the particles are touching one another allowing them to pass on their energy quickly.
- Metals are better thermal conductors than non-metals because metals have free electrons that can pass along thermal energy.