Difference between revisions of "Diffusion"
(→Lungs) |
(→Key Stage 4) |
||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[Diffusion]] is when [[substance]]s spread from a high [[concentration]] to a low [[concentration]] along the [[Concentration Gradient|concentration gradient]]. | [[Diffusion]] is when [[substance]]s spread from a high [[concentration]] to a low [[concentration]] along the [[Concentration Gradient|concentration gradient]]. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
Revision as of 08:45, 5 June 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Diffusion is when particles spread from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
About Diffusion
- Diffusion can only happen in a fluid which means a liquid or a gas because the particles can move past each other.
- Diffusion cannot happen in a solid because the particles are held in fixed positions.
- In diffusion the particles always spread from a high concentration where there is lots of the substance, to a low concentration where there is less of the substance.
- Diffusion stops when all substances are spread out equally and there is no longer a concentration gradient.
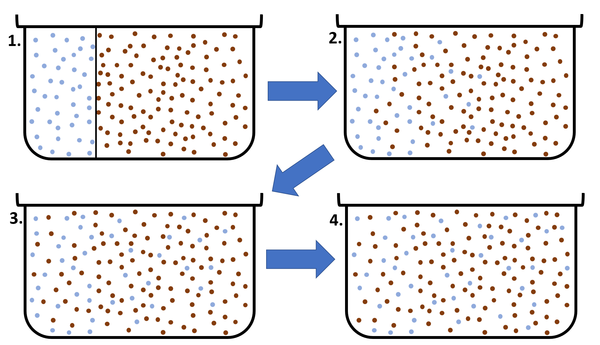
| This diagram shows a high concentration of blue particles on the left separated from the red particles by a barrier. When the barrier is removed the blue particles diffuse to the area of lower concentration on the right. Diffusion continues until all particles are equally spread. |
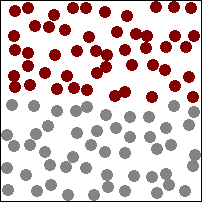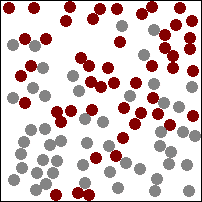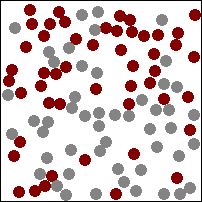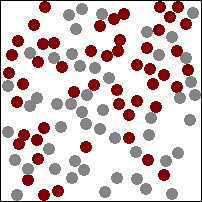
| This animation shows a high concentration of red particles initially at the top. When diffusion begins the red particles spread to the area of lower concentration at the bottom. Diffusion continues until all particles are equally spread. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Diffusion is when substances spread from a high concentration to a low concentration along the concentration gradient.