Difference between revisions of "Prokaryotic Cell"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Prokaryotic cells, pages 23, 38, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Prokaryotic cells, pages 23, 38, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
:[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Prokaryotic cells, pages 8-9, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Prokaryotic cells, pages 8-9, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Prokaryotic cells, page 10, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Prokaryotic cells, page 11, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''Prokaryotic cells, page 12, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Prokaryotic cells, pages 23, 24, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
Revision as of 14:57, 27 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
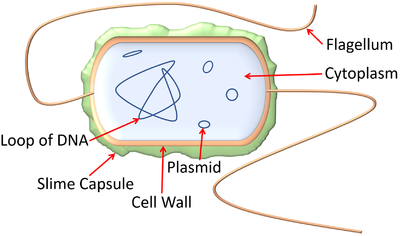
A prokaryotic cell is a simple cell which contains no membrane bound organelles.
About Prokaryotic Cells
- Prokaryotic cells include bacteria and some types of algae.
- Prokaryotic cells have a loop of DNA floating freely in the cytoplasm.
- Prokaryotic cells have no nucleus, mitochondria or chloroplasts.
- Prokaryotic cells are usually much smaller than eukaryotic cells.
- In the three domain system prokaryotes include both bacteria and archaea.
Examples
| A diagram showing an E.coli bacterium which is a prokaryote. |
References
AQA
- Prokaryotic cells, page 23, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Prokaryotic cells, page 23-4, 41, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Prokaryotic cells, pages 23, 38, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Prokaryotic cells, pages 8-9, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA