Difference between revisions of "Fuel Cell"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:FuelCell.png|right|300px|thumb|A [[diagram]] of a simple '''fuel cell'''.]] | ||
A '''fuel cell''' is a device which can combine [[Hydrogen]] and [[Oxygen]] to produce a [[Potential Difference]]. | A '''fuel cell''' is a device which can combine [[Hydrogen]] and [[Oxygen]] to produce a [[Potential Difference]]. | ||
===About Fuel Cells=== | ===About Fuel Cells=== | ||
| + | : In a '''fuel cell''' [[Oxygen]] is combined with [[Hydrogen]] to produce [[Water]]. | ||
| + | : '''Fuel cells''' are designed to combine [[Hydrogen Ion|Hydrogen ions]] and [[Hydroxide Ion|Hydroxide ions]] to produce a [[Potential Difference|potential difference]] between two [[electrode]]s. | ||
| + | : '''Fuel cells''' may be used in electric cars and were used on the [[Space Shuttle]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Advantages=== | ||
| + | *No [[Carbon Dioxide]] is produced. | ||
| + | *Refilling with [[Hydrogen]] is quicker than recharging a [[battery]]. | ||
| + | *They can be made in many different sizes for different uses. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Disadvantages=== | ||
| + | *[[Hydrogen]] must be stored as a [[Compressed Gas]]. | ||
| + | *[[Hydrogen]] is highly [[flammable]]. | ||
| + | *[[Hydrogen]] is made by [[electrolysis]] which requires [[electricity]], which is often made by power stations burning [[fuel]] and producing [[Carbon Dioxide]]. | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 15 January 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
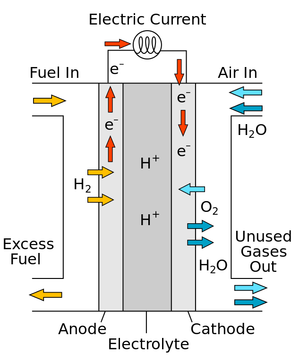
A diagram of a simple fuel cell.
A fuel cell is a device which can combine Hydrogen and Oxygen to produce a Potential Difference.
About Fuel Cells
- In a fuel cell Oxygen is combined with Hydrogen to produce Water.
- Fuel cells are designed to combine Hydrogen ions and Hydroxide ions to produce a potential difference between two electrodes.
- Fuel cells may be used in electric cars and were used on the Space Shuttle.
Advantages
- No Carbon Dioxide is produced.
- Refilling with Hydrogen is quicker than recharging a battery.
- They can be made in many different sizes for different uses.
Disadvantages
- Hydrogen must be stored as a Compressed Gas.
- Hydrogen is highly flammable.
- Hydrogen is made by electrolysis which requires electricity, which is often made by power stations burning fuel and producing Carbon Dioxide.