Key Stage 4
Meaning
Allotropes are different arrangements of atoms in an element.
About Allotropes
- Different allotropes of the same element can have very different physical properties such as melting point and electrical conductivity.
Examples
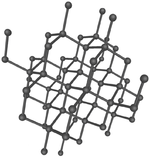
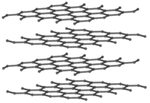
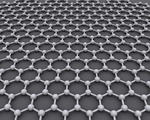
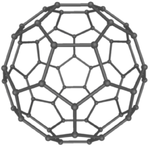
These are several allotropes of Carbon.
| Diamond is a giant covalent structure where each Carbon atom has 4 bonds with adjacent atoms. | Graphite has a giant covalent structure with each Carbon atom has 3 bonds with adjacent atoms in a layer with loose bonds between the layers. | Graphene has a giant covalent structure where each Carbon atom has 3 bonds with adjacent atoms forming a layer that is one atom thick. | Fullerenes have a giant covalent structure where each Carbon atom has 3 bonds with adjacent atoms forming a sphere. |