Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
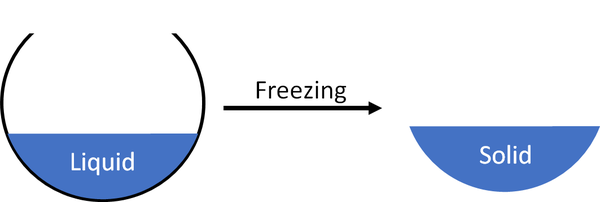
Freezing is when a liquid turns into a solid.
- Verb: To Freeze
- Present Participle: Freezing
| A liquid will freeze to become a solid. |
About Freezing
- A liquid can freeze when its gets cold enough.
- Freezing is a reversible process. When a liquid freezes you can always melt it back into a liquid.
- You may have seen these liquids freeze:
- Water
- Wax
| The water at this waterfall has frozen. | When the liquid wax drips down the side of a candle it freezes because it has cooled down. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Freezing is an exothermic process in which a liquid turns into a solid.
About Freezing
- Freezing is a reversible process. When a liquid freezes you can always melt it back into a liquid.
- You can make a liquid freeze by cooling it.
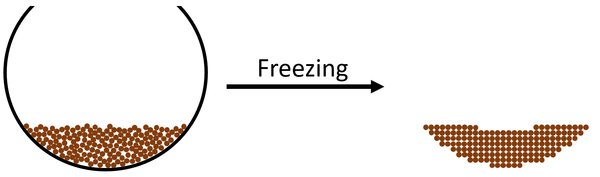
| The particles in the liquid slow down until they are slow enough that forces between the particles start to hold them in fixed positions. The particles become stuck in fixed positions which makes the state a solid. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Freezing is an exothermic physical change in which a liquid turns into a solid.
About Freezing
- Freezing happens when the particles in a liquid form bonds holding them in fixed positions as they lose potential energy.
- The temperature at which a substance freezes is the same as the temperature at which it melts so it is the melting point.
- Freezing is an exothermic process, which means it emits energy when it takes place.
- Freezing is a physical change, which means it is reversible and does not produce new chemicals.
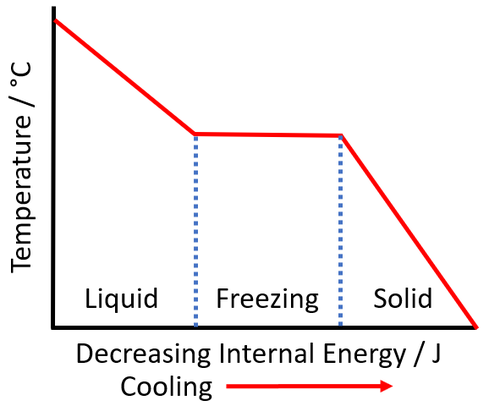
| As a liquid is cooled the internal energy decreases. As the liquid freezes the temperature of the substance stays the same. |