Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Reactivity is how vigorously a chemical will react.
About Reactivity
- Reactivity is determined by how easily an element can lose or gain electrons.
- Electrons are held in orbit around the nucleus because the electrons are negatively charged and are attracted to the nucleus which is positively charged.
- If an element loses electrons easily it is highly reactive.
- If an element gains electrons readily it is also highly reactive.
Three important factors affect reactivity of elements.
- The charge of the nucleus
- The shielding effect of inner electrons.
- Distance between the nucleus and the outer shell.
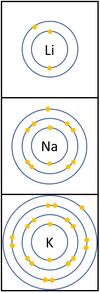
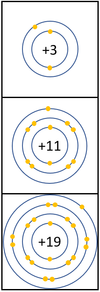
Reactivity in Groups 1, 2 and 3
| In a chemical reaction the electron in the outer shell is lost.
The reactivity increases as you go down the group because:
|
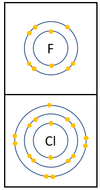
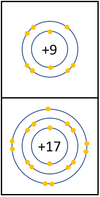
Reactivity in Group 7
| In a chemical reaction an extra electron is added to the outer shell.
The reactivity decreases as you go down the group because:
|