Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Anaerobic Respiration is the process of releasing stored chemical energy from sugars by breaking them down without Oxygen present.
About Aerobic Respiration
- In animal cells and plant cells and bacteria anaerobic respiration produces Lactic Acid.
- In yeast anaerobic respiration produces ethanol which is Alcohol (Drug).
- When bacteria or yeast use anaerobic respiration in food it is called fermentation.
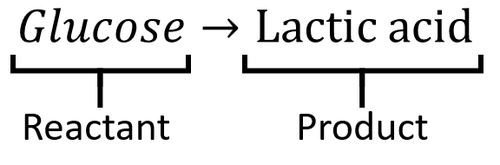
Word Equation
| A word equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells and plant cells and bacteria showing the reactants and products. |
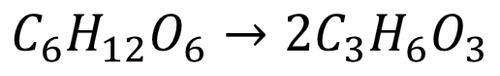
Symbol Equation
| A balanced symbol equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells and plant cells and bacteria. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Anaerobic Respiration is the process of releasing stored chemical energy from glucose in the absence of Oxygen.
About Anaerobic Respiration
- Aerobic respiration takes place in the muscles when they do not get enough Oxygen.
- Anaerobic respiration provides cells with the energy they need for protein synthesis, active transport and movement.
- In eukarytotic cells anaerobic respiration takes place in the mitochondria.
- In prokaryotic cells anaerobic respiration takes place in the cytoplasm of the cell.
- In animal cells and plant cells and bacteria anaerobic respiration produces Lactic Acid.
- In yeast anaerobic respiration produces ethanol which is Alcohol (Drug).
- When bacteria or yeast use anaerobic respiration in food it is called fermentation.
Word Equation
| A word equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells and plant cells and bacteria showing the reactants and products. |
Symbol Equation
| A balanced symbol equation for anaerobic respiration in animal cells and plant cells and bacteria. |