Key Stage 2
Meaning
Gas is a state of matter that can change size and shape to fit any container.
About Gases
- Most gases are invisible but we can feel them.
- When the air moves we call it the wind.
Gases are a state of matter that:
|
|
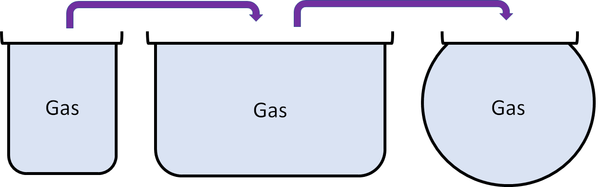
- Cannot hold their shape.
- Fit the shape of their container.
- Can be poured and will flow.
|
|
|
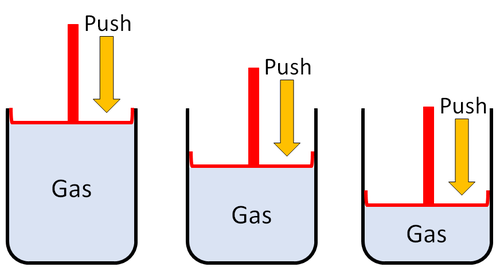
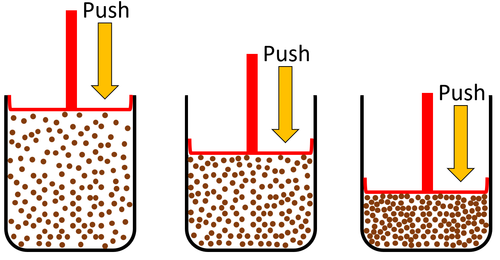
| Gases can be squashed into a smaller size.
|
Examples of gas materials:
- Air (A mixture of gases, mostly nitrogen and oxygen)
- Steam
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Gas is a State of Matter in which the particles are separated by large distances and can move freely.
About Gases
|
|
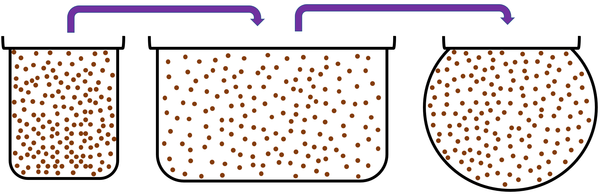
- Gases cannot hold their shape because the particles are free to move.
- Gases fit the shape of their containers because the particles are free to move.
- A gas can be poured and will flow because the particles are free to move.
|
|
|
| Gas can be squashed into a smaller size because the particles are spread apart.
|
Key Stage 4
Meaning
About Gases
- When a substance is in its gaseous state it is always less dense than in its liquid or gaseous state.
- A substance which is gaseous at room temperature has a smaller force of attraction between particles than a substance which is liquid or solid at room temperature.