Difference between revisions of "Proportional"
(Created page with "==Key Stage 4== ===Meaning=== When two variables are proportional they change together by a constant amount. ===About Proportional Graphs=== : A Scatter Graph|scatt...") |
|||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
: On a [[proportional]] [[Scatter Graph|scatter graph]] when one [[variable]] increases, the other increase or when one increases the other decreases. | : On a [[proportional]] [[Scatter Graph|scatter graph]] when one [[variable]] increases, the other increase or when one increases the other decreases. | ||
: A [[proportional]] graph may have a non-zero [[y-intercept]]. | : A [[proportional]] graph may have a non-zero [[y-intercept]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:ProportionalSketchGraph1.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:ProportionalSketchGraph2.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:DirectlyProportionalSketchGraph.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
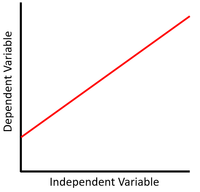
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[Scatter Graph|scatter graph]] shows a [[linear]] relationship that is [[proportional]] where x increases, y increases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>y = mx + c</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where m, the [[gradient]], is positive. | ||
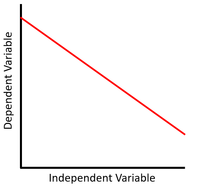
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[Scatter Graph|scatter graph]] shows a [[linear]] relationship that is [[proportional]] where x increases, y decreases. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>y = mx + c</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where m, the [[gradient]], is negative. | ||
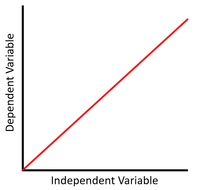
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[Scatter Graph|scatter graph]] shows a [[linear]] relationship that is [[Directly Proportional|directly proportional]] where x doubles, y doubles. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>y = mx</math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Where m, the [[gradient]], is positive. | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 10:28, 25 March 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
When two variables are proportional they change together by a constant amount.
About Proportional Graphs
- A scatter graph showing a proportional relationship has a linear gradient.
- On a proportional scatter graph when one variable increases, the other increase or when one increases the other decreases.
- A proportional graph may have a non-zero y-intercept.
Examples
| This scatter graph shows a linear relationship that is proportional where x increases, y increases.
\(y = mx + c\) Where m, the gradient, is positive. |
This scatter graph shows a linear relationship that is proportional where x increases, y decreases.
\(y = mx + c\) Where m, the gradient, is negative. |
This scatter graph shows a linear relationship that is directly proportional where x doubles, y doubles.
\(y = mx\) Where m, the gradient, is positive. |