Difference between revisions of "Red Blood Cell"
(→Adaptations of Red Blood Cells) |
(→Meaning) |
||
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
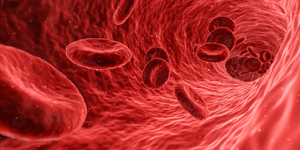
[[File:Blood.png|right|300px|thumb|A magnified image of blood going through a capillary.]] | [[File:Blood.png|right|300px|thumb|A magnified image of blood going through a capillary.]] | ||
| − | A '''red blood cell''' is [[Specialised Cell|specialised cell]] which carries [[oxygen]] around the body. | + | A '''red blood cell''' is a [[Specialised Cell|specialised cell]] which carries [[oxygen]] around the body. |
| + | |||
===Adaptations of Red Blood Cells=== | ===Adaptations of Red Blood Cells=== | ||
: '''Red blood cells''' are shaped to fit through [[capillary|capillaries]] without getting stuck. | : '''Red blood cells''' are shaped to fit through [[capillary|capillaries]] without getting stuck. | ||
| Line 9: | Line 10: | ||
===About Red Blood Cells=== | ===About Red Blood Cells=== | ||
| − | : [[Blood]] is a [[tissue]] made of [[Plasma | + | : [[Blood]] is a [[tissue]] made of [[Blood Plasma|plasma]], [[White Blood Cell|white blood cells]] and '''red blood cells'''. |
: '''Red blood cells''' are specially [[Adaptation|adapted]] to transfer [[oxygen]] around the body. | : '''Red blood cells''' are specially [[Adaptation|adapted]] to transfer [[oxygen]] around the body. | ||
| Line 19: | Line 20: | ||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:Blood.png|right|300px|thumb|A magnified image of blood going through a capillary.]] | ||
A '''red blood cell''' is a [[Specialised Animal Cell|specialised animal cell]] used to transport [[oxygen]] around the body. | A '''red blood cell''' is a [[Specialised Animal Cell|specialised animal cell]] used to transport [[oxygen]] around the body. | ||
===Adaptations of Red Blood Cells=== | ===Adaptations of Red Blood Cells=== | ||
| − | : '''Red blood cells''' have a | + | : '''Red blood cells''' have a biconcave shape which maximises their [[Surface Area|surface area]] to allow [[oxygen]] to be [[Absorb (Biology)|absorbed]] quickly. |
: '''Red blood cells''' have a smooth rounded edge to pass through the [[capillaries]] without getting stuck. | : '''Red blood cells''' have a smooth rounded edge to pass through the [[capillaries]] without getting stuck. | ||
: '''Red blood cells''' have a large number of [[haemoglobin]] [[molecule]]s used to transport [[oxygen]]. | : '''Red blood cells''' have a large number of [[haemoglobin]] [[molecule]]s used to transport [[oxygen]]. | ||
| Line 28: | Line 30: | ||
===About Red Blood Cells=== | ===About Red Blood Cells=== | ||
| + | : '''Red blood cells''' make up about 45% of the [[blood]]. | ||
: '''Red blood cells''' carry [[oxygen]] in their [[haemoglobin]] [[molecule]]s. | : '''Red blood cells''' carry [[oxygen]] in their [[haemoglobin]] [[molecule]]s. | ||
: '''Red blood cells''' are made in the [[Bone Marrow|bone marrow]]. | : '''Red blood cells''' are made in the [[Bone Marrow|bone marrow]]. | ||
| − | : When '''red blood cells''' die they are broken into small pieces called [[ | + | : When '''red blood cells''' die they are broken into small pieces called [[platelet]]s which help the [[blood]] clot when there is an open wound. |
: If a person suffers from [[Sickle Cell Anemia]] the '''red blood cells''' are sickle shaped so they can become stuck in [[capillaries]]. | : If a person suffers from [[Sickle Cell Anemia]] the '''red blood cells''' are sickle shaped so they can become stuck in [[capillaries]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:BloodConstituents.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
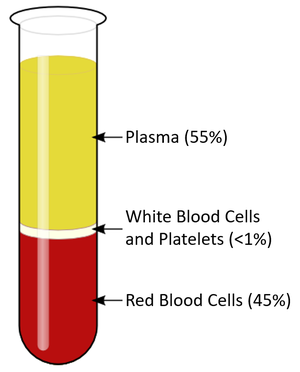
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the [[percentage]]s of the different parts that make up [[blood]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f473 ''Red blood cell, pages 86, 89, 107, 116-7, 118, 149, 253, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10234 ''Red blood cells, page 32, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Red blood cells, page 36, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Red blood cells, page 80, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Red blood cells, page 86, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851338/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851338&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=425855d5890466e47189e1c21b67a1ea ''Red blood cells, pages 34, 55, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Red blood cells, pages 52, 61, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Red blood cells, pages 54-5, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Red blood cells (erythrocytes), page 157, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Red blood cells (erythrocytes), page 167, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Red blood cells, page 262, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Red blood cells, page 61, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''Red blood cells, page 89, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Red blood cells, page 31, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Red blood cells, page 38, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Red blood cells, pages 28, 31, 61, 67-68, 77, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:21, 20 February 2022
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A red blood cell is a specialised cell which carries oxygen around the body.
Adaptations of Red Blood Cells
- Red blood cells are shaped to fit through capillaries without getting stuck.
- Red blood cells are shaped to have a large surface area.
- Red blood cells have no nucleus to provide a bigger volume inside to store oxygen.
About Red Blood Cells
- Blood is a tissue made of plasma, white blood cells and red blood cells.
- Red blood cells are specially adapted to transfer oxygen around the body.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A red blood cell is a specialised animal cell used to transport oxygen around the body.
Adaptations of Red Blood Cells
- Red blood cells have a biconcave shape which maximises their surface area to allow oxygen to be absorbed quickly.
- Red blood cells have a smooth rounded edge to pass through the capillaries without getting stuck.
- Red blood cells have a large number of haemoglobin molecules used to transport oxygen.
- Red blood cells have lost their nucleus to allow extra space for haemoglobin molecules.
About Red Blood Cells
- Red blood cells make up about 45% of the blood.
- Red blood cells carry oxygen in their haemoglobin molecules.
- Red blood cells are made in the bone marrow.
- When red blood cells die they are broken into small pieces called platelets which help the blood clot when there is an open wound.
- If a person suffers from Sickle Cell Anemia the red blood cells are sickle shaped so they can become stuck in capillaries.
| A diagram showing the percentages of the different parts that make up blood. |
References
AQA
- Red blood cell, pages 86, 89, 107, 116-7, 118, 149, 253, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Red blood cells, page 32, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Red blood cells, page 36, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Red blood cells, page 80, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Red blood cells, page 86, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Red blood cells, pages 34, 55, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- Red blood cells, pages 52, 61, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Red blood cells, pages 54-5, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Red blood cells (erythrocytes), page 157, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Red blood cells (erythrocytes), page 167, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Red blood cells, page 262, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Red blood cells, page 61, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Red blood cells, page 89, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel