Difference between revisions of "Weight"
(→Key Stage 3) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
===About Weight=== | ===About Weight=== | ||
: Weight is a [[force]] so it is [[Measure|measured]] in [[Newton]]s. | : Weight is a [[force]] so it is [[Measure|measured]] in [[Newton]]s. | ||
| − | : Weight is a [[Non-contact Force|non-contact force]]. | + | : Weight is a [[Non-contact Force|non-contact force]] because an [[object]] does not need to be touching the ground to be [[attract]]ed to the [[Earth]]. |
: Weight always acts downwards. | : Weight always acts downwards. | ||
: All [[object]]s on [[Earth]] have [[weight]] because the [[Earth]] has a [[Gravitational Field|gravitational field]]. | : All [[object]]s on [[Earth]] have [[weight]] because the [[Earth]] has a [[Gravitational Field|gravitational field]]. | ||
: Different [[planet]]s have a different strength [[Gravitational Field|gravitational field]], so the same [[object]] might '''weigh''' a different amount on different [[planet]]s. | : Different [[planet]]s have a different strength [[Gravitational Field|gravitational field]], so the same [[object]] might '''weigh''' a different amount on different [[planet]]s. | ||
| − | + | : On [[Earth]] the [[Gravitational Field Strength|gravitational field strength]] is roughly 10[[N/kg]] | |
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 61: | Line 61: | ||
: m = Mass | : m = Mass | ||
: g = Gravitational Field Strength | : g = Gravitational Field Strength | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Example Calculations=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''Calculate the [[weight]] of a 25[[kg]] object on [[Earth]].''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''A 550[[kg]] space probe is sent into deep space beyond the gravitational field of any other [[object]]. Calculate the weight of the space probe.''' | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |'''[[The Moon]] has a [[Gravitational Field Strength|gravitational field strength]] of 1.6[[N/kg]]. Calculate the weight of a 85[[kg]] astronaut on [[The Moon]]. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | m = 25[[kg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | g<sub>Earth</sub> = 10[[N/kg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = m \times g </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = 25 \times 10 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = 250N </math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | m = 550[[kg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | g<sub>Deep Space</sub> = 0[[N/kg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = m \times g </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = 550 \times 0 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = 0N </math> | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:left;" | | ||
| + | m = 85[[kg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | g<sub>The Moon</sub> = 1.6[[N/kg]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = m \times g </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = 85 \times 1.6 </math> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <math>W = 136N </math> | ||
| + | |} | ||
Revision as of 12:42, 15 October 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
Weight is how heavy or light something is.
About Weight
- Objects have weight because of the gravity of the Earth.
- Weight can be measured using a Newton Meter or a Measuring Scale.
- Weight is measured in Newtons but can also be measured in stone, pounds and ounces.
- Weight depends on the amount of mass an object has.
| Golf Ball | Beach Ball | Bowling Ball |
| The Golf Ball is not made of much material so it is lightest. | The Beach Ball might be the biggest but it is not the heaviest. | The Bowling Ball is made of the most material, so it is the heaviest. |
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Weight is the the force on an object that is in a gravitational field.
About Weight
- Weight is a force so it is measured in Newtons.
- Weight is a non-contact force because an object does not need to be touching the ground to be attracted to the Earth.
- Weight always acts downwards.
- All objects on Earth have weight because the Earth has a gravitational field.
- Different planets have a different strength gravitational field, so the same object might weigh a different amount on different planets.
- On Earth the gravitational field strength is roughly 10N/kg
Examples
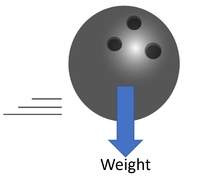
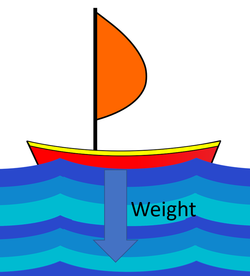
| Weight makes a tennis ball fall to the ground. | Weight holds the bowling ball to the ground. | If the weight of a boat were bigger than the upthrust the boat would sink. |
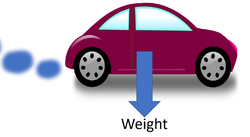
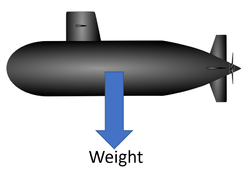
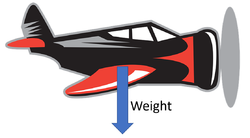
| The weight of the car acts from its centre of mass. | The submarine has the same weight under the water as it would on land, but in the water this is balanced by the upthrust. | Planes can be very heavy but their weight is balanced by the lift. |
Equation
- Weight = Mass x Gravitational Field Strength
\[W = m \times g \] Where:
- W = Weight
- m = Mass
- g = Gravitational Field Strength
Example Calculations
| Calculate the weight of a 25kg object on Earth. | A 550kg space probe is sent into deep space beyond the gravitational field of any other object. Calculate the weight of the space probe. | The Moon has a gravitational field strength of 1.6N/kg. Calculate the weight of a 85kg astronaut on The Moon. |
|
m = 25kg gEarth = 10N/kg \(W = m \times g \) \(W = 25 \times 10 \) \(W = 250N \) |
m = 550kg gDeep Space = 0N/kg \(W = m \times g \) \(W = 550 \times 0 \) \(W = 0N \) |
m = 85kg gThe Moon = 1.6N/kg \(W = m \times g \) \(W = 85 \times 1.6 \) \(W = 136N \) |