Difference between revisions of "White Blood Cell"
(→Adaptations of White Blood Cells) |
|||
| (8 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
[[White Blood Cell]]s are [[Specialised Animal Cell|specialised animal cells]] which protect the body from [[pathogen]]s. | [[White Blood Cell]]s are [[Specialised Animal Cell|specialised animal cells]] which protect the body from [[pathogen]]s. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About White Blood Cells=== | ||
| + | : '''White blood cells''' make up less than 1% of the [[blood]]. | ||
| + | : '''White blood cells''' are produced in the [[Bone Marrow|bone marrow]]. | ||
| + | : '''White blood cells''' can weaken and kill [[pathogen]]s including [[virus]]es, [[Pathogenic Fungus|fungi]], [[Pathogenic Bacteria|bacteria]] and [[Pathogenic Protist|protists]]. | ||
| + | There are two main types of '''white blood cell''' that you should know: | ||
| + | *[[Phagocyte]]s - Which engulf and then break down [[pathogen]]s. | ||
| + | *[[Lymphocyte]]s - Which produce [[Antibody|antibodies]] which attach themselves to [[pathogen]]s to make it easier for the [[phagocyte]]s to engulf them and produce [[antitoxin]]s to cancel out the effects of [[toxic]] [[chemical]]s made by the [[pathogen]]s. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:WhiteBloodCell.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:LymphocyteClipart.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A drawing of a [[phagocyte]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A drawing of a [[lymphocyte]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:BloodConstituents.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
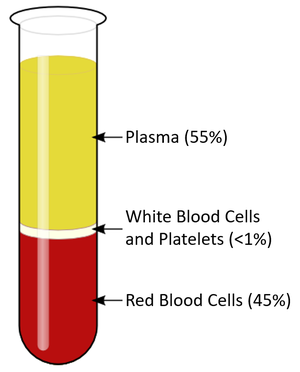
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |A [[diagram]] showing the [[percentage]]s of the different parts that make up [[blood]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f611 ''White blood cells, page 150-1, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''White blood cells, page 55, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10438 ''White blood cells, pages 32, 46, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''White blood cells, pages 36, 49, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''White blood cells, pages 53, 91, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851338/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851338&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=425855d5890466e47189e1c21b67a1ea ''White blood cells, pages 55, 87-8, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''White blood cells, pages 81, 130, 131, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''White blood cells, pages 87, 136, 137, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''White blood cells, pages 103, 167, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''White blood cells, pages 164-167, 263, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''White blood cells, pages 41, 42, 61, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''White blood cells, pages 58, 59, 89, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''White blood cells, page 95, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''White blood cells, pages 31, 71, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''White blood cells, pages 77, 223, 226, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 12:09, 25 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A white blood cell is a specialised cell which is used to fight infection.
Adaptations of White Blood Cells
- White blood cells have a large nucleus to make antibodies to fight infection.
About White Blood Cells
- White blood cells are part of the immune system.
- White blood cells are specially adapted to fight infection.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
White Blood Cells are specialised animal cells which protect the body from pathogens.
About White Blood Cells
- White blood cells make up less than 1% of the blood.
- White blood cells are produced in the bone marrow.
- White blood cells can weaken and kill pathogens including viruses, fungi, bacteria and protists.
There are two main types of white blood cell that you should know:
- Phagocytes - Which engulf and then break down pathogens.
- Lymphocytes - Which produce antibodies which attach themselves to pathogens to make it easier for the phagocytes to engulf them and produce antitoxins to cancel out the effects of toxic chemicals made by the pathogens.
| A drawing of a phagocyte. | A drawing of a lymphocyte. |
| A diagram showing the percentages of the different parts that make up blood. |
References
AQA
- White blood cells, page 150-1, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- White blood cells, page 55, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- White blood cells, pages 32, 46, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- White blood cells, pages 36, 49, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- White blood cells, pages 53, 91, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- White blood cells, pages 55, 87-8, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
- White blood cells, pages 81, 130, 131, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- White blood cells, pages 87, 136, 137, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- White blood cells, pages 103, 167, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- White blood cells, pages 164-167, 263, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- White blood cells, pages 41, 42, 61, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- White blood cells, pages 58, 59, 89, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel