Key Stage 3
Meaning
A carbohydrate is a nutrient in our diets that is used in the body for respiration.
About Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates can be split into two groups. Complex Carbohydrates like starch which are very important in our diet and Simple Carbohydrates called sugars that can be harmful if we eat to much of them.
Sugar
Sugar Molecules
- Sugar molecules are simple and the body can quickly get energy from them.
- You should know:
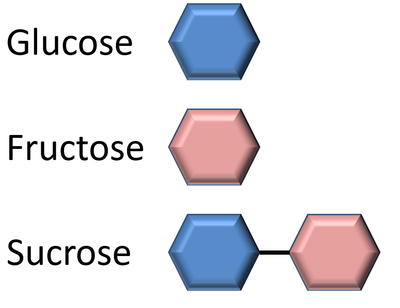
- Glucose - A sugar found in syrup and sweets.
- Fructose - A sugar found in fruits.
- Sucrose - Found in white sugar which is made of one glucose molecule and one fructose molecule bonded together.
|
|
| There are many different sugar molecules. These are just three examples.
|
Sugar in foods
Foods with lots of sugars:
|
|
|
|
|
| Fruit has lots of sugar but is healthy because it also has vitamins and fibre inside.
|
Yoghurt has a lot of sugar but there are also some health parts like a mineral called Calcium.
|
Sweets are full of sugar with nothing healthy in them.
|
Energy drinks have nothing healthy in them and are packed with sugar.
|
Testing For Sugars
- Glucose and Fructose can be detected with the Benedict's Test.
- Sucrose cannot be detected with the Benedict's Test unless you first react it with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Method
- 1. A sample of food is dissolved in water.
- 2. The solution is added to blue Benedict's solution in a boiling tube.
- 3. The solution is kept at 90°C for up to 10 minutes.
- 4. A colour change indicates the presence of glucose or fructose. If they are present the solution will eventually turn brick red or brown.
|
|
| When sugar is present the Benedict's solution turns from blue through several colours until it becomes brick red or brown.
If this was done with sucrose the Benedict's solution would stay blue.
|
Starch
Starch Molecule
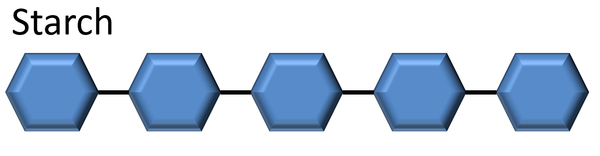
- Starch is made of hundreds of glucose molecules bonded together.
|
|
| A starch molecule made of many smaller glucose molecules.
|
Starch in Foods
Foods with lots of starch:
|
|
|
|
|
| Bread makes part of a balanced diet because it has a lot of stored energy we can use.
|
A balanced diet might contain pasta for energy.
|
Potatoes are an excellent source of energy in a balanced diet.
|
Rice is a very important part of many people's balanced diet.
|
Testing for Starch
- Starch can be detected using Iodine Solution.
Method
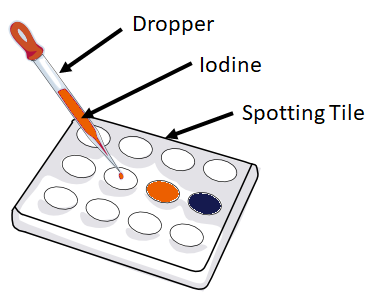
- 1. A small sample of food is placed on a spotting tile.
- 2. A drop of Iodine Solution is added to the food sample.
- 3. If the Iodine solution turns from orange to blue-black then the food contains starch.
|
|
| Iodine solution is an orange liquid. When the iodine solution is added to starch the iodine solution turns from orange to blue-black.
|
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A carbohydrate is a nutrient in our diets that is used in the body for respiration.
About Carbohydrates
- Carbohydrates can be split into three groups. Monosaccharides which are simple sugars, disaccharides which are made from two monosaccharides bonded together and polysaccharides which are many monosaccharides bonded together.
Monosaccharides
Monosaccharide Molecules
- Monosaccharides are all isomers with the formula C6H12O6.
The three main monosaccharides are:
Testing For Monosaccharides
- Monosaccharides can be detected with the Benedict's Test.
- Disaccharides cannot be detected with the Benedict's Test unless you first react it with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Method
- 1. A sample of food is dissolved in water.
- 2. The solution is added to blue Benedict's solution in a boiling tube.
- 3. The solution is kept at 90°C for up to 10 minutes.
- 4. A colour change indicates the presence of glucose or fructose. If they are present the solution will eventually turn brick red or brown.
|
|
| When sugar is present the Benedict's solution turns from blue through several colours until it becomes brick red or brown.
If this was done with sucrose the Benedict's solution would stay blue.
|
Disaccharides
Disaccharide Molecules
- Disaccharides are all isomers with the formula C12H22O11.
The two Disaccharides you might know are:
Polysaccharides
- Polysaccharides are all long chains of simpler monosaccharides bonded together.
Some polysaccharides you should know are:
Starch
Starch Molecule
- Starch is made of hundreds of glucose molecules bonded together.
|
|
| A starch molecule made of many smaller glucose molecules.
|
Testing for Starch
- Starch can be detected using Iodine Solution.
Method
- 1. A small sample of food is placed on a spotting tile.
- 2. A drop of Iodine Solution is added to the food sample.
- 3. If the Iodine solution turns from orange to blue-black then the food contains starch.
|
|
| Iodine solution is an orange liquid. When the iodine solution is added to starch the iodine solution turns from orange to blue-black.
|
References
AQA
- Carbohydrate, pages 55, 56, 100-104, 182, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Carbohydrates, page 193, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Carbohydrates, pages 40, 46, 128-129, 136, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
Edexcel
- Carbohydrates, page 17, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Carbohydrates, page 176, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Carbohydrates, page 18, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Carbohydrates, page 293, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Carbohydrates, page 41, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Carbohydrates, page 20, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Carbohydrates, page 23, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Carbohydrates, page 38, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Carbohydrates, pages 65, 245, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Carbohydrates; testing for, page 24, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR