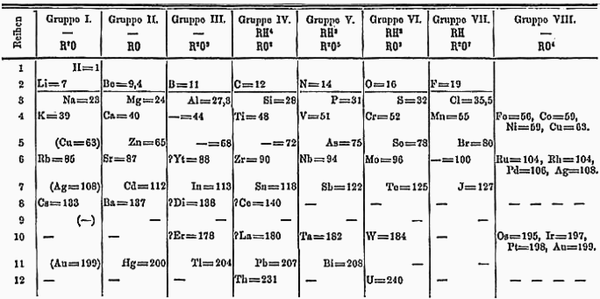
Mendeleev's Periodic Table
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Mendeleev's Periodic Table is the basis for the modern Periodic Table but arranged elements by Relative Atomic Mass instead of Atomic Number.
About Mendeleev's Periodic Table
- Scientists always try to look for patterns to help arrange complicated problems. Many different elements had been discovered so scientists wanted to arrange them based on patterns they noticed. Some scientists arranged them by patterns in chemical properties while others tried to arrange them by patterns in Physical Properties like Melting Point or Relative Atomic Mass.
- In 1808 a scientist called John Dalton, who created the Dalton Model of the atom, arranged elements by their Relative Atomic Mass.
- In 1864 a scientist called John Newlands arranged elements by Relative Atomic Mass but because he noticed that ever 8th element had similar chemical properties he arranged them into what he called 'octaves'. However, he had not taken into account the possibility that some elements had not been discovered, so he placed some elements into the wrong groups just to fit the pattern he thought he had seen.
- In 1869 Mendeleev was the first to place gaps where the elements did not fit the pattern but still arranged them by both their chemical properties and Relative Atomic Mass. This enabled Mendeleev to predict the existence of elements that had not yet been discovered.
- Mendeleev's Periodic Table was proven (nearly) correct when new elements were discovered that fit in the the gaps he had left. This ability of his table to predict the properties of new elements was what convinced other scientists his Periodic Table was (nearly) correct.
- There were some problems with Mendeleev's Periodic Table that kept scientists skeptical of it. One such problem was that Argon has a greater Relative Atomic Mass than Potassium which would put Argon in the Alkali Metals.
- Once the structure of the atom was investigated by physicists in the early 1900s it was discovered how to correct Mendeleev's Periodic Tableby ordering the elements by Atomic Number instead of Relative Atomic Mass. This produced the modern Periodic Table.