Thermistor
Contents
Key Stage 4
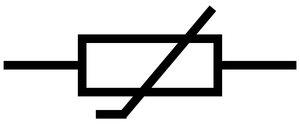
Meaning
A thermistor is a resistor which changes resistance depending on the temperature.
About Thermistors
- 'NTC' thermistors decrease resistance as the temperature increases. (NTC = Negative Temperature Coefficient.)
- A thermistor can be used to control the current passing through a circuit. If the potential difference is constant then the current decreases as temperature decreases.
- A thermistor can be used to control the potential difference of another component in series with it. If the temperature is decreased then the potential difference across other components will decrease.
- Thermistors can be used temperature sensors.
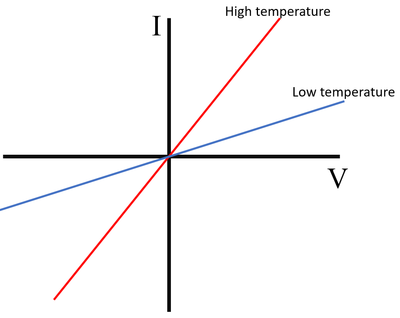
IV Graph
Description
The IV Graph for an 'NTC' thermistor shows that:
- At a high temperature the current increases rapidly with the potential difference
- At a low temperature the current increases slowly with the potential difference.
Explanation
- The resistance of an 'NTC' thermistor increases as the temperature decreases.
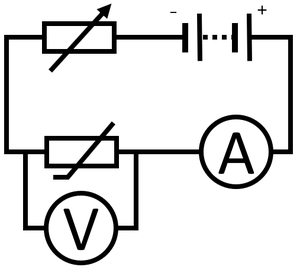
Obtaining the IV Graph
|
References
AQA
- Thermistor, pages 47, 52, 64-5, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Thermistors, page 184, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thermistors, page 27, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Thermistors, page 57, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 293, 298-9, 316-17, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 43-4, 64-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 60, 80, 81, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Thermistors, pages 62, 82, 83, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
Edexcel
- Thermistors, page 149, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Thermistors, page 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Thermistors, page 74, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Thermistors, pages 225, 226, 229, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel