Difference between revisions of "Cell Nucleus"
(Created page with "The part of the cell containing DNA which provides instructions for how the cell should behave.") |
|||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | The part of the [[cell]] | + | ==Key Stage 3== |
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | [[File:Cell.png|right|300px|thumb|The '''nucleus''' can be seen in the centre of this [[Cell (Biology)|cell]].]] | ||
| + | The '''nucleus''' is the part of the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] that contains [[DNA]] which provides instructions for how the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] should behave. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Singular [[Noun]]: '''Nucleus''' | ||
| + | Plural [[Noun]]: '''Nuclei''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Function=== | ||
| + | The '''nucleus''' controls the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Nucleus=== | ||
| + | : The '''nucleus''' contains the genetic material of a cell. | ||
| + | : '''Nuclei''' are found in [[Plant Cell|plant cells]] and [[Animal Cell|animal cells]] but not in [[Bacteria]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:OnionCells.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MuscleCells.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
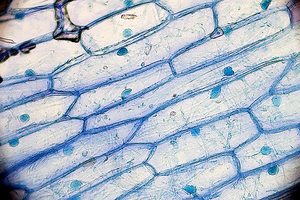
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The '''nuclei''' of these cells can be seen stained blue. | ||
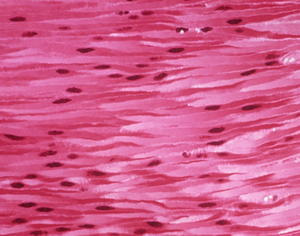
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The '''nuclei''' of these cells is a darker pink than the rest of the cells. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SpermCellClipart.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:PalisadeCellClipart.png|center|150px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The '''nucleus''' in this [[Sperm Cell|sperm cell]] is very large compared to the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A picture of a [[Palisade Cell|palisade cell]] showing several parts including the '''nucleus'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | A '''nucleus''' is a [[Membrane Bound Organelle|membrane bound organelle]] found in [[Eukaryotic Cell|eukaryotic cells]] containing the [[DNA]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Function=== | ||
| + | : The '''nucleus''' contains [[DNA]] which controls the actions of the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] and provides the information to make copies of the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About the Nucleus=== | ||
| + | : The '''nucleus''' contains [[gene]]s which determine which [[protein]]s are [[Protein Synthesis|synthesised]] in the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| + | : During [[mitosis]] before the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]] [[Cell Division|divides]] the [[membrane]] of the '''nucleus''' [[dissolve]]s to release two sets of [[chromosome]]s which then form two identical '''nuclei'''. | ||
| + | : '''Nuclei''' are found in [[Animal Cell|animal cells]], [[Plant Cell|plant cells]], [[Fungal Cell|fungal cells]] and [[protist]]s but are not found in [[bacteria]] or [[archaea]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Examples=== | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:OnionCells.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:MuscleCells.png|center|300px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The '''nuclei''' of these cells can be seen stained blue. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The '''nuclei''' of these cells is a darker pink than the rest of the cells. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:SpermCellClipart.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | |[[File:PalisadeCellClipart.png|center|150px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |The '''nucleus''' in this [[Sperm Cell|sperm cell]] is very large compared to the [[Cell (Biology)|cell]]. | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:300px; text-align:center;" |A picture of a [[Palisade Cell|palisade cell]] showing several parts including the '''nucleus'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Nucleus, page 11, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Nucleus, pages 110, 132-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Nucleus, pages 12-3, 22, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Nucleus, pages 23, 33, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Nucleus, pages 23, 33, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Nucleus, pages 5, 13-17, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Nucleus, pages 6-7, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Nucleus; radius, pages 22-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Nucleus, page 162, 355, 380, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Nucleus, page 18, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Nucleus, page 49, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Nucleus, pages 90, 140, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Nucleus (atoms), pages 20, 170-172, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Nucleus (cells), page 18, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:43, 15 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
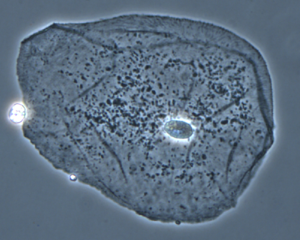
The nucleus can be seen in the centre of this cell.
The nucleus is the part of the cell that contains DNA which provides instructions for how the cell should behave.
Singular Noun: Nucleus Plural Noun: Nuclei
Function
The nucleus controls the cell.
About the Nucleus
- The nucleus contains the genetic material of a cell.
- Nuclei are found in plant cells and animal cells but not in Bacteria.
Examples
| The nuclei of these cells can be seen stained blue. | The nuclei of these cells is a darker pink than the rest of the cells. |
| The nucleus in this sperm cell is very large compared to the cell. | A picture of a palisade cell showing several parts including the nucleus. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A nucleus is a membrane bound organelle found in eukaryotic cells containing the DNA.
Function
- The nucleus contains DNA which controls the actions of the cell and provides the information to make copies of the cell.
About the Nucleus
- The nucleus contains genes which determine which proteins are synthesised in the cell.
- During mitosis before the cell divides the membrane of the nucleus dissolves to release two sets of chromosomes which then form two identical nuclei.
- Nuclei are found in animal cells, plant cells, fungal cells and protists but are not found in bacteria or archaea.
Examples
| The nuclei of these cells can be seen stained blue. | The nuclei of these cells is a darker pink than the rest of the cells. |
| The nucleus in this sperm cell is very large compared to the cell. | A picture of a palisade cell showing several parts including the nucleus. |
References
AQA
- Nucleus, page 11, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Nucleus, pages 110, 132-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Nucleus, pages 12-3, 22, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Nucleus, pages 23, 33, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Nucleus, pages 23, 33, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Nucleus, pages 5, 13-17, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Nucleus, pages 6-7, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Nucleus; radius, pages 22-3, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
Edexcel
- Nucleus, page 162, 355, 380, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Nucleus, page 18, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Nucleus, page 49, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Nucleus, pages 90, 140, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel