Difference between revisions of "Orbit"
| (7 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
==Key Stage 3== | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| − | An [[Orbit]] is the path an [[asteroid]], [[comet]], [[planet]] or [[dwarf planet]] takes around a [[star]] and the path a [[moon]] takes around a [[planet]]. | + | An [[Orbit]] is the path an [[asteroid]], [[comet]], [[planet]] or [[Dwarf Planet|dwarf planet]] takes around a [[star]] and the path a [[moon]] takes around a [[planet]]. |
===About Orbits=== | ===About Orbits=== | ||
: [[Moon]]s [[orbit]] [[planet]]s and [[planet]]s [[orbit]] the [[stars]] due to [[gravity]]. | : [[Moon]]s [[orbit]] [[planet]]s and [[planet]]s [[orbit]] the [[stars]] due to [[gravity]]. | ||
| − | : [[Isaac Newton|Newton]] was the first person to realise that [[object]]s were held in [[orbit]] by [[gravity]] which he [[explain]]ed in his [[Newton's Universal | + | : [[Isaac Newton|Newton]] was the first person to realise that [[object]]s were held in [[orbit]] by [[gravity]] which he [[explain]]ed in his [[Newton's Law of Universal Gravitation|Law of Universal Gravitation]]. |
: [[Gravity]] is a constant [[force]] directed to the centre of a [[massive]] [[object]]. | : [[Gravity]] is a constant [[force]] directed to the centre of a [[massive]] [[object]]. | ||
: [[The Moon]] feels a [[force]] pulling it towards the centre of the [[Earth]]. The [[Earth]] feels a [[force]] equal in [[magnitude]] but opposite in direction to that of [[The Moon]]. | : [[The Moon]] feels a [[force]] pulling it towards the centre of the [[Earth]]. The [[Earth]] feels a [[force]] equal in [[magnitude]] but opposite in direction to that of [[The Moon]]. | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
''Higher'' | ''Higher'' | ||
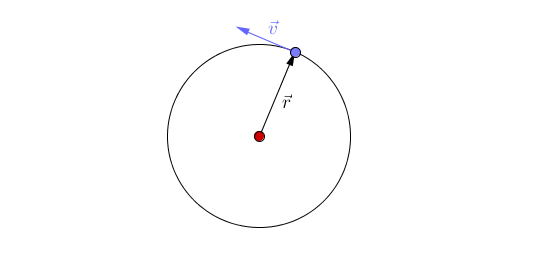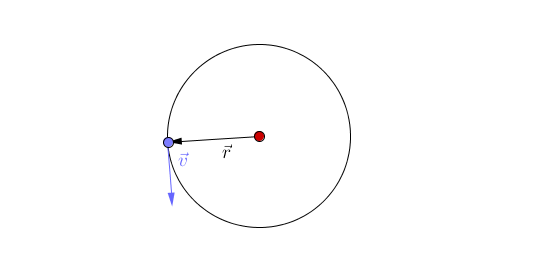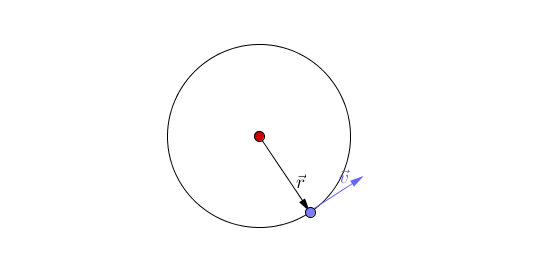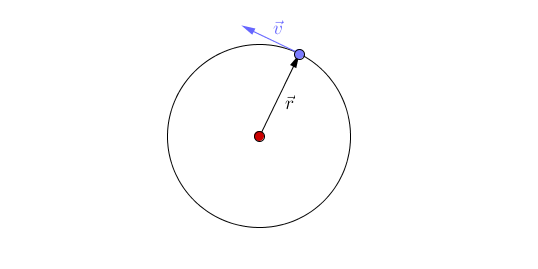
: There are two types of [[orbit]] you should know: | : There are two types of [[orbit]] you should know: | ||
| − | :*Circular [[orbit]] - An [[orbit]] where the distance between the two [[object]]s (the | + | :*Circular [[orbit]] - An [[orbit]] where the distance between the two [[object]]s (the radius) remains constant. In this [[orbit]] the [[speed]] of the [[orbit]]ting [[object]] is constant. However, the [[velocity]] of the [[orbit]]ting [[object]] is constantly changing due to the changing direction. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
|[[File:CircularMotion.gif|center|]] | |[[File:CircularMotion.gif|center|]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows [[acceleration]] due to the changing direction of a circular [[orbit]] of the blue [[object]] around the red [[object]]. A circular [[orbit]] is one of constant | + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows [[acceleration]] due to the changing direction of a circular [[orbit]] of the blue [[object]] around the red [[object]]. A circular [[orbit]] is one of constant radius. |
|} | |} | ||
| Line 55: | Line 55: | ||
|[[File:Orbit1.gif|center|400px]] | |[[File:Orbit1.gif|center|400px]] | ||
|- | |- | ||
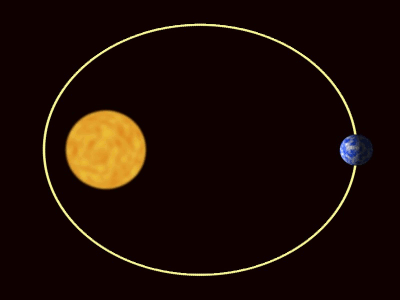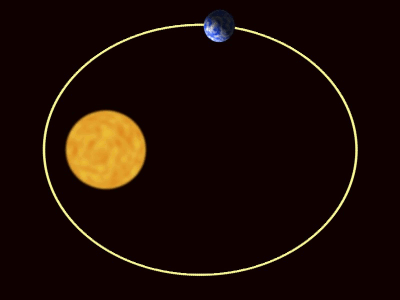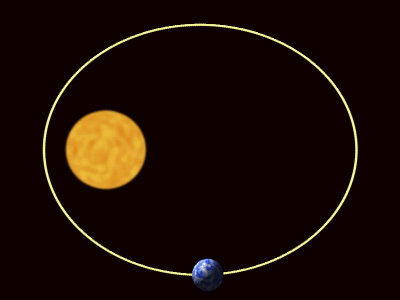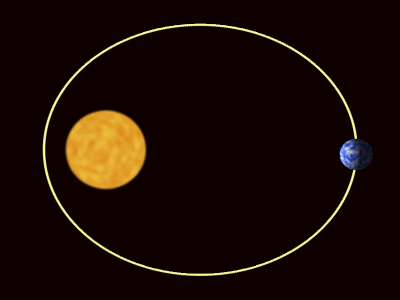
| − | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:center;" |This | + | | style="height:20px; width:400px; text-align:center;" |This animation shows the elliptical [[orbit]] of a [[planet]] around a [[Star]]. As the [[planet]] gets further from the [[Star]] the [[speed]] of the [[planet]] decreases. As the [[planet]] gets closer to the [[Star]] the [[speed]] of the [[planet]] increases. |
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Orbit, pages 276, 278-9, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac350 ''Orbits, page 101, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Orbits, pages 236-237, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Orbits, pages 249-50, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Orbits, pages 320, 321, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Orbits; circular, pages 253-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Orbits; speed of, pages 254-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945733/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945733&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=2a2dbec9db6bf5766c0458d908fa0a52 ''Orbits, page 59, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120223/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120223&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=068ecf40278c32406a7f1c6e66751417 ''Orbits, pages 118, 120-121, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948163/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948163&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=0fdbfd5dd397d6e24a9dfb250f08587f ''Orbits, pages 184-186, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945687/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945687&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a598e52189317a20311d7a632747bc9 ''Orbits, page 97, Gateway GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359837/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359837&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3c4229e8b023b2b60768e7ea2307cc6f ''Orbits, pages 240-241, Gateway GCSE Physics, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 07:55, 15 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
An Orbit is the path planet takes around a star and the path a moon takes around a planet.
| A Planet orbiting a Star. |
About Orbits
- An orbit is a roughly circular path, but can be stretched out into an oval shape.
- The Moon orbits the Earth. This means The Moon takes a circular path around the Earth.
- All the planets orbit The Sun. This means the planets take a circular path around The Sun.
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An Orbit is the path an asteroid, comet, planet or dwarf planet takes around a star and the path a moon takes around a planet.
About Orbits
- Moons orbit planets and planets orbit the stars due to gravity.
- Newton was the first person to realise that objects were held in orbit by gravity which he explained in his Law of Universal Gravitation.
- Gravity is a constant force directed to the centre of a massive object.
- The Moon feels a force pulling it towards the centre of the Earth. The Earth feels a force equal in magnitude but opposite in direction to that of The Moon.
| The planets are pulled towards The Sun by gravity. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
An orbit is the circular or elliptical path that an object takes a more massive object due to a force of attraction acting between them.
About Orbits
- Orbits are caused by a force of attraction between two objects acting towards their centres.
- Planets orbit Stars due to the force of gravity.
Higher
- There are two types of orbit you should know:
| This animation shows acceleration due to the changing direction of a circular orbit of the blue object around the red object. A circular orbit is one of constant radius. |
| This animation shows the elliptical orbit of a planet around a Star. As the planet gets further from the Star the speed of the planet decreases. As the planet gets closer to the Star the speed of the planet increases. |
References
AQA
- Orbit, pages 276, 278-9, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Orbits, page 101, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Orbits, pages 236-237, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Orbits, pages 249-50, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Orbits, pages 320, 321, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA
- Orbits; circular, pages 253-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Orbits; speed of, pages 254-5, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Orbits, page 59, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Orbits, pages 118, 120-121, GCSE Physics, Pearson Edexcel
- Orbits, pages 184-186, GCSE Physics, CGP, Edexcel