Difference between revisions of "Chemical Reaction"
(→Examples) |
|||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" | | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" | | ||
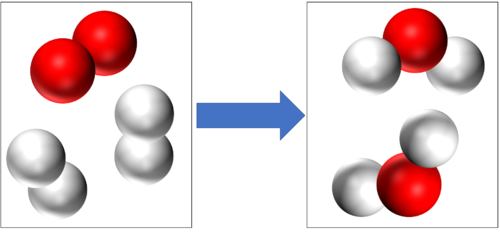
| − | Hydrogen + Oxygen → Water | + | [[Hydrogen]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Water]] |
2H<sub>2</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O | 2H<sub>2</sub> + O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O | ||
| Line 39: | Line 39: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" | | | style="height:20px; width:500px; text-align:center;" | | ||
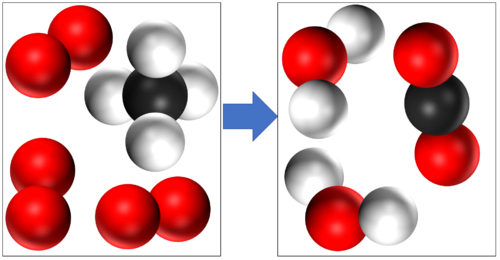
| − | Methane + Oxygen → Water + Carbon Dioxide | + | [[Methane]] + [[Oxygen]] → [[Water]] + [[Carbon Dioxide]] |
CH<sub>4</sub> + 2O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O + CO<sub>2</sub> | CH<sub>4</sub> + 2O<sub>2</sub> → 2H<sub>2</sub>O + CO<sub>2</sub> | ||
|} | |} | ||
Revision as of 18:48, 23 September 2018
Contents
Key Stage 2
Meaning
A chemical reaction is when one substance changes into another.
About Chemical Reactions
- Most chemical reactions are irreversible.
- Chemical reactions usually cause a change in temperature.
- Chemical reactions you should know are:
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A Chemical Reaction is when the atoms in molecules break their bonds and form new bonds, usually with other atoms.
About Chemical Reactions
- Most chemical reactions are irreversible.
- In a chemical reaction the atoms rearrange to form a new substance.
- Chemical reactions often need some energy to start, like combustion where the fuel needs to be heated to start.
- If a chemical reaction gives off more energy than it needs to start then it is called an Exothermic Reaction. In these reactions the temperature increases.
- If a chemical reaction takes in more energy than it gives out then it is called an Endothermic Reaction.
In these reactions the temperature decreases.
Examples
|
2H2 + O2 → 2H2O |
|
Methane + Oxygen → Water + Carbon Dioxide CH4 + 2O2 → 2H2O + CO2 |