Difference between revisions of "Monomer"
(→Examples) |
(→About Monomers) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
: Different [[monomer]]s are used to produce different [[polymer]]s. | : Different [[monomer]]s are used to produce different [[polymer]]s. | ||
There are several [[monomer]]s that you may know: | There are several [[monomer]]s that you may know: | ||
| − | *[[Glucose]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in a [[Condensation Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]s; [[ | + | *[[Glucose]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in a [[Condensation Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]s; [[Starch]] and [[Glycogen]]. |
| − | *[[Amino Acid]]s - This [[monomer]] comes together in a [[Condensation Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]s known as [[ | + | *[[Amino Acid]]s - This [[monomer]] comes together in a [[Condensation Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]s known as [[Protein]]s. |
*[[Nucleotide]]s - This [[monomer]] comes together in a [[Condensation Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[DNA]]. | *[[Nucleotide]]s - This [[monomer]] comes together in a [[Condensation Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[DNA]]. | ||
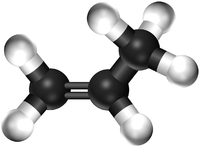
| − | *[[Ethene]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in an [[Addition Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[ | + | *[[Ethene]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in an [[Addition Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[Polythene]]. |
| − | *[[Propene]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in an [[Addition Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[ | + | *[[Propene]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in an [[Addition Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[Polypropene]]. |
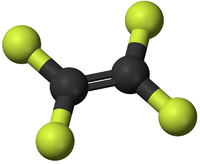
| − | *[[ | + | *[[TetraFluoroEthene]] - This [[monomer]] comes together in an [[Addition Polymerisation]] to form the [[polymer]]; [[PolyTetraFluoroEthene]]. |
===Examples=== | ===Examples=== | ||
Revision as of 13:05, 18 January 2019
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A monomer is as small molecule that can bond with other molecules to form a polymer.
About Monomers
There are several monomers that you may know:
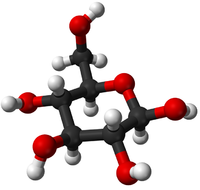
- Glucose - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymers; Starch and Glycogen.
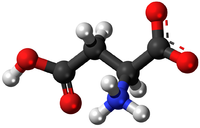
- Amino Acids - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymers known as Proteins.
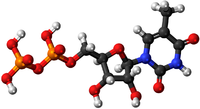
- Nucleotides - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymer; DNA.
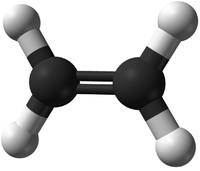
- Ethene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; Polythene.
- Propene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; Polypropene.
- TetraFluoroEthene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; PolyTetraFluoroEthene.
Examples
| Glucose | Amino Acid | Nucleotide |
| Ethene | Propene | Tetrafluoroethene |