Difference between revisions of "Extracting Metals by Electrolysis"
(→Key Stage 3) |
|||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
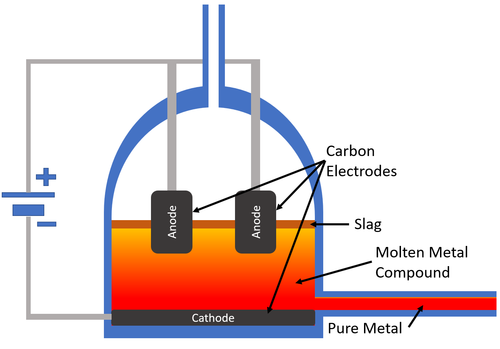
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Carbon]] [[electrode]]s are used to pass an [[Electrical Current]] through the [[molten]] [[mineral]]. The [[metal]] collects at the [[cathode]] which carries a negative [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and the [[pure]] [[metal]] is removed from the [[Electrolysis Cell|electrolysis cell]]. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |[[Carbon]] [[electrode]]s are used to pass an [[Electrical Current]] through the [[molten]] [[mineral]]. The [[metal]] collects at the [[cathode]] which carries a negative [[Electrical Charge|charge]] and the [[pure]] [[metal]] is removed from the [[Electrolysis Cell|electrolysis cell]]. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | '''Extraction of metals by electrolysis''' is a method of obtaining a [[metal]] from a [[mineral]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Extracting Metals by Electrolysis=== | ||
| + | : '''Electrolysis''' is usually used to [[Extraction of Metals|extract metals]] when the [[metal]] is more [[Reactivity Series|reactive]] than [[Carbon]] or the [[mineral]] is [[soluble]] in [[water]] making it cheaper to '''extract by electrolysis''' than by [[smelting]]. | ||
Revision as of 12:04, 25 January 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
Electrolysis is a way to extract metals from minerals when the metal is more reactive than Carbon.
About Extracting Metals by Electrolysis
- Metals that are more reactive than Carbon cannot be displaced with Carbon so electrolysis is used to extract them.
| Carbon electrodes are used to pass an Electrical Current through the molten mineral. The metal collects at the cathode which carries a negative charge and the pure metal is removed from the electrolysis cell. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Extraction of metals by electrolysis is a method of obtaining a metal from a mineral.