Difference between revisions of "Enzyme"
| (9 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | ==Key Stage 3== | ||
| + | ===Meaning=== | ||
| + | An [[enzyme]] is a biological [[molecule]] which can speed up a [[Chemical Reaction|reaction]] or break down large [[molecule]]s into smaller ones. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===About Enzymes=== | ||
| + | : [[Organism]]s have a number of different [[enzyme]]s that control the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reactions]] that take place inside the [[cytoplasm]]. | ||
| + | : [[Digestive Enzyme|Digestive '''enzymes''']] are used to break down large [[insoluble]] food [[molecule]]s into small [[soluble]] [[molecule]]s. | ||
| + | : The [[chemical]]s that an [[enzyme]] affects are called [[Substrate (Biology)|substrates]]. | ||
| + | : [[Enzyme]]s have an area called an [[Active Site|active site]] which is where the [[enzyme]] interacts with the [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]]. | ||
| + | : The [[Active Site|active site]] is shaped to fit with only one [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]] so [[enzyme]]s all have specific roles in an [[organism]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:EnzymeDiagram.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
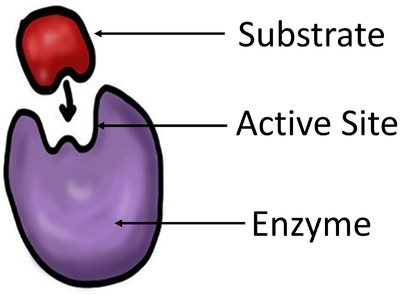
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows an [[enzyme]], [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]] and the [[Active Site|active site]] of the [[enzyme]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
==Key Stage 4== | ==Key Stage 4== | ||
===Meaning=== | ===Meaning=== | ||
| Line 6: | Line 24: | ||
: [[Organism]]s have a number of different [[enzyme]]s that control the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reactions]] that take place inside the [[cytoplasm]]. | : [[Organism]]s have a number of different [[enzyme]]s that control the [[Chemical Reaction|chemical reactions]] that take place inside the [[cytoplasm]]. | ||
: [[Digestive Enzyme|Digestive '''enzymes''']] are used to break down large insoluble food [[molecule]]s into small [[soluble]] [[molecule]]s. | : [[Digestive Enzyme|Digestive '''enzymes''']] are used to break down large insoluble food [[molecule]]s into small [[soluble]] [[molecule]]s. | ||
| + | : The [[chemical]]s that an [[enzyme]] affects are called [[Substrate (Biology)|substrates]]. | ||
| + | : [[Enzyme]]s have an area called an [[Active Site|active site]] which is where the [[enzyme]] interacts with the [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]]. | ||
| + | : The [[Active Site|active site]] is shaped to fit with only one [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]] so [[enzyme]]s all have specific roles in an [[organism]]. | ||
| + | : The fact that certain [[enzyme]]s only work on certain [[Substrate (Biology)|substrates]] is explained by the [[Lock and Key Model]]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:EnzymeDiagram.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows an [[enzyme]], [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]] and the [[Active Site|active site]] of the [[enzyme]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Denaturation=== | ||
: [[Enzyme]]s can be [[denature]]d if the [[temperature]]s are too high or the [[pH]] is too extreme. Different [[enzyme]]s have a different [[Optimum|optimum]] [[temperature]] and [[Optimum|optimum]] [[pH]]. | : [[Enzyme]]s can be [[denature]]d if the [[temperature]]s are too high or the [[pH]] is too extreme. Different [[enzyme]]s have a different [[Optimum|optimum]] [[temperature]] and [[Optimum|optimum]] [[pH]]. | ||
| + | : When an [[enzyme]] is [[denature]]d it changes shape so that the [[Substrate (Biology)|substrate]] will no longer fit the [[Active Site|active site]]. | ||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[File:DenaturedEnzyme.png|center|400px]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
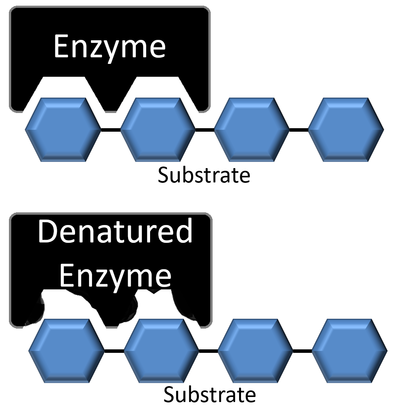
| + | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[diagram]] shows an [[enzyme]] before and after [[denature|denaturation]]. | ||
| + | |} | ||
===pH and Enzymes=== | ===pH and Enzymes=== | ||
| Line 27: | Line 65: | ||
| style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[graph]] shows the [[optimum]] [[temperature]] for many [[enzyme]]s in the [[human]] body. | | style="height:20px; width:200px; text-align:center;" |This [[graph]] shows the [[optimum]] [[temperature]] for many [[enzyme]]s in the [[human]] body. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | : If the [[temperature]] goes above | + | : If the [[temperature]] goes above 45 all of the [[enzyme]]s will be [[denature]]d. |
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Enzyme, pages 207, 243, 253, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158754/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158754&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=27ad53b0283feeff7fc5ae04a9e205f266 ''Enzyme, pages 64, 86-7, 96-103, 109, 170, 190, 246, 346-9, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Enzymes, page 154, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=5ec5fc3f6429e30c1d9ab9bca2bccf93 ''Enzymes, pages 109-111, 114-116, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945954/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945954&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=100574c08fbbb64318256eb79ed61a76 ''Enzymes, pages 115- 117, 120-122, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851362/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851362&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=7d78d70a2044ee9982dae010c94af92a ''Enzymes, pages 125, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe09915 ''Enzymes, pages 25-27, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945563/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945563&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9a1d023a374038e6072f33c4f3cf808b ''Enzymes, pages 28-31, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359373/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359373&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=952a73bbb09d222ecc4b50d200679849 ''Enzymes, pages 38-39, 42-49, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851338/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851338&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=425855d5890466e47189e1c21b67a1ea ''Enzymes, pages 43, 45-50, 65, 125-6, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====Edexcel==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948147/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948147&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f63dcd8345f4e49c717b39a228a36c7c ''Enzymes, page 239, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Enzymes, pages 143, 176, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945741/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945741&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=30da4f2178da182547b62a7329d13b57 ''Enzymes, pages 15-17, 133, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''Enzymes, pages 16-18, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Enzymes, pages 36-42, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Enzymes, pages 8, 12-13, 257, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Enzymes, pages 8, 12-13, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945725/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945725&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=694be7494de75af3349537d34e13f7f0 ''Enzymes, pages 82, 103, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Enzymes; action, pages 18-19, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120207/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120207&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=22455ff53961978667722edaa64c0be5 ''Enzymes; activity, pages 20-21, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120215/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120215&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=8f96ddb76196848bafdb124354e4cf77 ''Enzymes; denaturing, page 143, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1292120193/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1292120193&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=572df39392fb4200db8391d98ae6314e ''Enzymes; denaturing, page 257, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946748/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946748&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a4f0348fc37d0ba1bb52d27f8679581f ''Enzymes; investigating activity, page 17, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782948120/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782948120&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=dedef775c6a43dbb0a609441525adac0 ''Enzymes; investigating activity, pages 39, 40, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel ''] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====OCR==== | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945679/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945679&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a2db42f7b4bdf10cafaafa3bb9120940 ''Enzymes, page 72, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Enzymes, pages 15-17, 133, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Enzymes, pages 17-19, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359829/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359829&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=90e8d7b4f039d53035238fa0320fe00b ''Enzymes, pages 183, 204, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359810/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359810&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=d768d99f1a06f7c12fab40e5aef85a55 ''Enzymes, pages 32-35, 38, 144, 256-257, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Enzymes; factors affecting enzymes, pages 15, 16, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Enzymes; factors affecting, page 18, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945695/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945695&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ceafcc80bcad6b6754ee97a0c7ceea53 ''Enzymes; investigating activity of, page 17, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945660/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945660&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=83aa4500ad7759e7f401a1c5ba5df758 ''Enzymes; investigating activity, page 19, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR ''] | ||
Latest revision as of 14:56, 6 December 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
An enzyme is a biological molecule which can speed up a reaction or break down large molecules into smaller ones.
About Enzymes
- Organisms have a number of different enzymes that control the chemical reactions that take place inside the cytoplasm.
- Digestive enzymes are used to break down large insoluble food molecules into small soluble molecules.
- The chemicals that an enzyme affects are called substrates.
- Enzymes have an area called an active site which is where the enzyme interacts with the substrate.
- The active site is shaped to fit with only one substrate so enzymes all have specific roles in an organism.
| This diagram shows an enzyme, substrate and the active site of the enzyme. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
Enzymes are large proteins that can act as a catalyst for chemical reactions or be used to break down large molecules into smaller ones.
About Enzymes
- Organisms have a number of different enzymes that control the chemical reactions that take place inside the cytoplasm.
- Digestive enzymes are used to break down large insoluble food molecules into small soluble molecules.
- The chemicals that an enzyme affects are called substrates.
- Enzymes have an area called an active site which is where the enzyme interacts with the substrate.
- The active site is shaped to fit with only one substrate so enzymes all have specific roles in an organism.
- The fact that certain enzymes only work on certain substrates is explained by the Lock and Key Model.
| This diagram shows an enzyme, substrate and the active site of the enzyme. |
Denaturation
- Enzymes can be denatured if the temperatures are too high or the pH is too extreme. Different enzymes have a different optimum temperature and optimum pH.
- When an enzyme is denatured it changes shape so that the substrate will no longer fit the active site.
| This diagram shows an enzyme before and after denaturation. |
pH and Enzymes
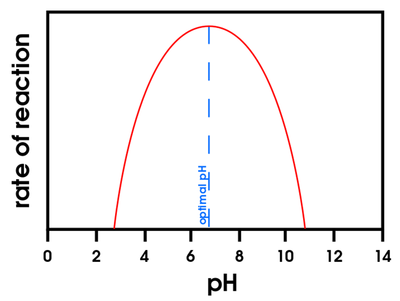
- Enzymes have an optimum pH at which they work best. If the pH is far from this optimum value the enzyme will denature.
| This graph shows the optimum pH for amylase. |
Temperature and Enzymes
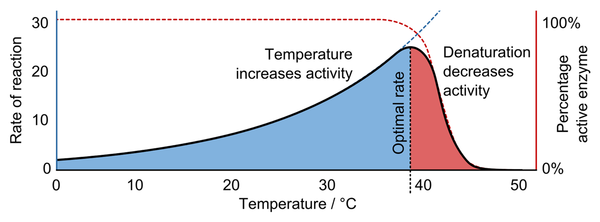
- Enzymes have an optimum temperature at which they work best. If the temperature is far above this optimum value the enzyme will denature. If the temperature is far lower the rate of reaction slows down due to the number of particle collisions being lower at lower temperatures.
| This graph shows the optimum temperature for many enzymes in the human body. |
- If the temperature goes above 45 all of the enzymes will be denatured.
References
AQA
- Enzyme, pages 207, 243, 253, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Enzyme, pages 64, 86-7, 96-103, 109, 170, 190, 246, 346-9, GCSE Biology; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Enzymes, page 154, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 109-111, 114-116, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Biology, CGP, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 115- 117, 120-122, GCSE Biology, CGP, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 125, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 2, Hodder, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 25-27, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 28-31, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 38-39, 42-49, GCSE Biology; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Enzymes, pages 43, 45-50, 65, 125-6, GCSE Biology, Hodder, AQA
Edexcel
- Enzymes, page 239, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 143, 176, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 15-17, 133, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 16-18, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 36-42, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 8, 12-13, 257, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 8, 12-13, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Enzymes, pages 82, 103, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Enzymes; action, pages 18-19, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Enzymes; activity, pages 20-21, GCSE Biology, Pearson, Edexcel
- Enzymes; denaturing, page 143, GCSE Chemistry, Pearson, Edexcel
- Enzymes; denaturing, page 257, GCSE Combined Science, Pearson Edexcel
- Enzymes; investigating activity, page 17, GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, Edexcel
- Enzymes; investigating activity, pages 39, 40, GCSE Biology, CGP, Edexcel
OCR
- Enzymes, page 72, Gateway GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Enzymes, pages 15-17, 133, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Enzymes, pages 17-19, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Enzymes, pages 183, 204, Gateway GCSE Chemistry, Oxford, OCR
- Enzymes, pages 32-35, 38, 144, 256-257, Gateway GCSE Biology, Oxford, OCR
- Enzymes; factors affecting enzymes, pages 15, 16, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Enzymes; factors affecting, page 18, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Enzymes; investigating activity of, page 17, Gateway GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR
- Enzymes; investigating activity, page 19, Gateway GCSE Biology; The Revision Guide, CGP, OCR