Difference between revisions of "Parallel Circuit"
(→Resistors in Parallel) |
|||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
The [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] between points A and B is 6Ω. | The [[Electrical Resistance|resistance]] between points A and B is 6Ω. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158770/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158770&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ec31595e720e1529e49876c3866fff6e ''Parallel circuit, pages 54-5, 62-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac81 ''Parallel circuits, page 29, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Parallel circuits, page 302, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945598/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945598&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=ad276ad49df77ab4b40ab4fd0fe10139 ''Parallel circuits, pages 186, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/178294558X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=178294558X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=f0dfb66dafcb0c6e9449e7b1a4ae1ac353 ''Parallel circuits, pages 29, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851370/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851370&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=01c69b0ae058f809cf636033e6ba793e ''Parallel circuits, pages 37, 47, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/019835939X/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=019835939X&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=57e96876985fc39b1a3d8a3e3dc238b6 ''Parallel circuits, pages 60-61, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782946403/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782946403&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=32a0abb60dff015b15b50e9b1d7b4644 ''Parallel circuits, pages 72-76, 78, 79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945970/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945970&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a120d24dcc7cc7a58192069a3aafc1d2 ''Parallel circuits, pages 74-78, 80, 81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 16:20, 10 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 3
Meaning
A Parallel Circuit is an electrical circuit with two or more paths the current can flow along.
About Parallel Circuits
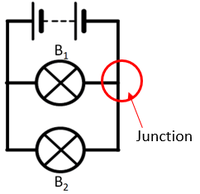
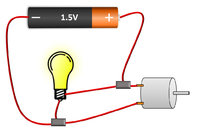
- In a parallel circuit the current is split at junctions before taking a different path.
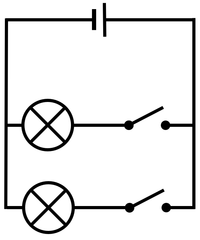
- Switches can be placed in a Parallel Circuit to allow current along one path at a time.
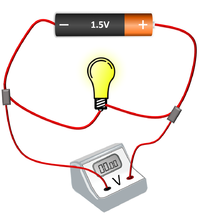
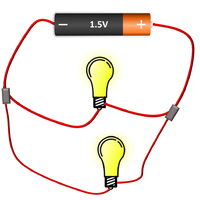
- Components placed in parallel with each other have the same Potential Difference across them.
| The current from the battery splits at the junction sharing the current between the two bulbs. | The two bulbs in this parallel circuit can be switched on and off separately. |
Examples
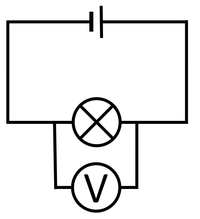
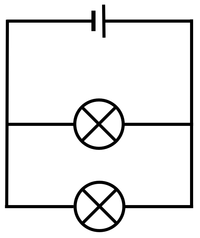
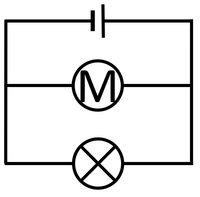
| The cell, bulb and voltmeter are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them. | The two bulbs are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. | The bulb and motor are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. |
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A Parallel Circuit is an electrical circuit with two or more paths the current can flow along.
About Parallel Circuits
- In a parallel circuit the current is split at junctions before taking a different path.
- Switches can be placed in a parallel circuit to allow current along one path at a time.
- Components placed in parallel with each other have the same potential difference across them.
| The current from the battery splits at the junction sharing the current between the two bulbs. | The two bulbs in this parallel circuit can be switched on and off separately. |
Examples
| The cell, bulb and voltmeter are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them. | The two bulbs are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. | The bulb and motor are in parallel so they have the same potential difference across them but may have a different current passing through them. |
Resistors in Parallel
NB: You only need to know what happens with identical resistors in parallel.
- When identical resistors are added in parallel there are more paths for the electricity so the resistance is reduced.
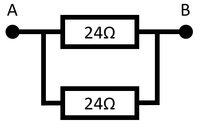
| Two identical resistors in parallel gives twice the number of paths, so has half the resistance.
The resistance between points A and B is 12Ω. |
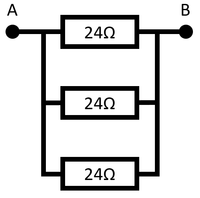
Three identical resistors in parallel gives three times the number of paths, so has a third of the resistance.
The resistance between points A and B is 8Ω. |
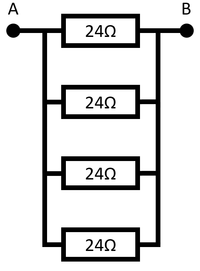
Four identical resistors in parallel gives four times the number of paths, so has a quarter of the resistance.
The resistance between points A and B is 6Ω. |
References
AQA
- Parallel circuit, pages 54-5, 62-3, GCSE Physics; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Parallel circuits, page 29, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, page 302, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 186, 187, GCSE Combined Science; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 29, 30, GCSE Physics; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 37, 47, GCSE Physics, Hodder, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 60-61, GCSE Physics; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 72-76, 78, 79, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy; Physics, CGP, AQA
- Parallel circuits, pages 74-78, 80, 81, GCSE Physics; The Complete 9-1 Course for AQA, CGP, AQA