Difference between revisions of "Mains Electricity"
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | : The [[Power Supply|power supply]] for the '''mains electricity''' is a variety of [[Energy Resource|energy resources]] including; [[Coal | + | : The [[Power Supply|power supply]] for the '''mains electricity''' is a variety of [[Energy Resource|energy resources]] including; [[Coal Power|Coal]], [[Gas Power|Natural Gas]], [[Nuclear Power]] and [[Wind Power|Wind]]. |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
|- | |- | ||
Revision as of 16:47, 8 April 2019
Key Stage 3
Meaning
The mains electricity is the electricity supply to houses, shops and factories.
Key Stage 4
Meaning
The mains electricity is the electricity supply to houses, shops and factories provided by the National Grid.
About Mains Electricity
- The mains in the houses in the UK provides a potential difference of 230V and provides a maximum current of 13A.
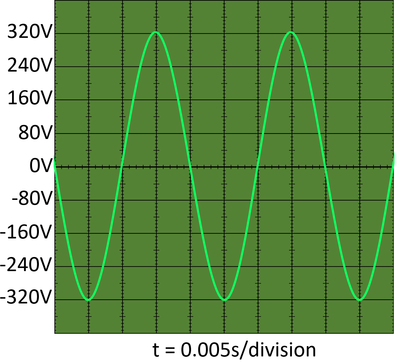
- The mains electricity is an alternating current with a frequency of 50Hz.
| An oscilloscope trace of mains electricity shows its frequency is 50Hz as the time period is 0.02s per oscillation and the peak potential difference is 320V, but the average over time is 230V. |
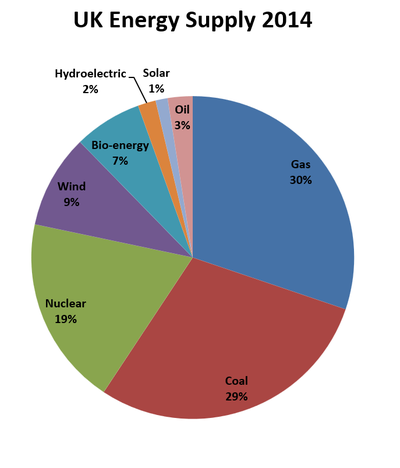
- The power supply for the mains electricity is a variety of energy resources including; Coal, Natural Gas, Nuclear Power and Wind.
| The percentage of the United Kingdom's electricity generated by different energy resources 2014 is shown in a pie chart. |