Difference between revisions of "Monomer"
(→About Monomers) |
|||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
|[[File:BallandStickTetrafluoroethene.png|center|200px]] | |[[File:BallandStickTetrafluoroethene.png|center|200px]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===References=== | ||
| + | ====AQA==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0008158762/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0008158762&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=a0fffa35b3ea49a63404f6704e0df7cc ''Monomer, pages 74-5, 246-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851354/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851354&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9012a0d354024419214fb3ad5ac44ba0 ''Monomers, page 158, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/0198359381/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=0198359381&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=47c8d1ae58d8b3a5e2094cd447154558 ''Monomers, pages 168-169, 224, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Monomers, pages 187, 263, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945962/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945962&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=476bb5c8d1dfb5c08ac81b6d4d1c98d8 ''Monomers, pages 236, 237, 241, 244, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1782945571/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1782945571&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=9e29fad914244909903e5e93f8a01d187 ''Monomers, pages 80, 83, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Monomers; of addition polymers, page 188, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
| + | :[https://www.amazon.co.uk/gp/product/1471851346/ref=as_li_tl?ie=UTF8&camp=1634&creative=6738&creativeASIN=1471851346&linkCode=as2&tag=nrjc-21&linkId=3ac654f4b0da781c49c855a1af4c92ea ''Monomers; of condensation polymers, page 191, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA ''] | ||
Revision as of 09:57, 9 November 2019
Contents
Key Stage 4
Meaning
A monomer is as small molecule that can bond with other molecules to form a polymer.
About Monomers
Foundation
There are some monomers that you may know:
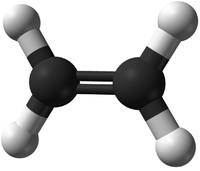
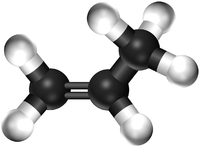
- Ethene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; Polythene.
- Propene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; Polypropene.
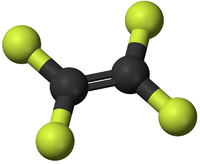
- TetraFluoroEthene - This monomer comes together in an Addition Polymerisation to form the polymer; PolyTetraFluoroEthene.
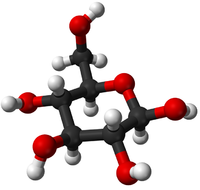
- Glucose - This monomer forms the polymers; Starch and Glycogen.
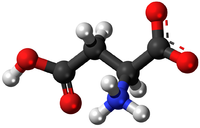
- Amino Acids - This monomer forms the polymers known as Proteins.
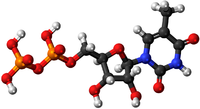
- Nucleotides - This monomer forms the polymer; DNA.
Higher
- Glucose - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymers; Starch and Glycogen.
- Amino Acids - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymers known as Proteins.
- Nucleotides - This monomer comes together in a Condensation Polymerisation to form the polymer; DNA.
Examples
| Glucose | Amino Acid | Nucleotide |
| Ethene | Propene | Tetrafluoroethene |
References
AQA
- Monomer, pages 74-5, 246-9, GCSE Chemistry; Student Book, Collins, AQA
- Monomers, page 158, GCSE Combined Science Trilogy 1, Hodder, AQA
- Monomers, pages 168-169, 224, GCSE Chemistry; Third Edition, Oxford University Press, AQA
- Monomers, pages 187, 263, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Monomers, pages 236, 237, 241, 244, GCSE Chemistry, CGP, AQA
- Monomers, pages 80, 83, GCSE Chemistry; The Revision Guide, CGP, AQA
- Monomers; of addition polymers, page 188, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA
- Monomers; of condensation polymers, page 191, GCSE Chemistry, Hodder, AQA